Road Freight Procurement Intelligence Report, 2024 - 2030 (Revenue Forecast, Supplier Ranking & Matrix, Emerging Technologies, Pricing Models, Cost Structure, Engagement & Operating Model, Competitive Landscape)
- Published Date: Jul, 2024
- Base Year for Estimate: 2023
- Report ID: GVR-P-10593
- Format: Electronic (PDF)
- Historical Data: 2021 - 2022
- Number of Pages: 60
Road Freight - Procurement Trends
“Increase in global trade activity, e-commerce expansion, and rise in retail sales are driving the expansion of the road freight market.”
Road freight procurement facilitates substantial benefits to businesses, such as flexibility, accessibility, cost-effectiveness, speed, and end-to-end connectivity. The global market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.5%, from 2024 to 2030. Road networks have a wide coverage, providing access to even remote areas. It allows flexible scheduling, enabling companies to adjust delivery times based on demand fluctuations or urgent requirements. Compared to other modes of transportation (such as rail or air), road freight transport requires less initial investment in infrastructure or specialized vehicles. It is generally faster for short to medium distances, as compared to other modes of transport. It also facilitates end-to-end connectivity by providing door-to-door service, eliminating the need for additional handling or trans-shipment.
The growth is being driven by drivers such as an increase in global trade activity, e-commerce expansion, rise in retail sales, improvement in transportation infrastructure, need for quicker deliveries, and growth of construction activities. For instance, road freight transport plays a crucial role in connecting production centers, distribution hubs, and end consumers for trade activities. On a similar note, the rapid rise of e-commerce has led to a surge in the need for efficient and timely delivery services. This has significantly boosted the demand for this industry, especially for last-mile delivery services. Moreover, modern consumers are increasingly demanding fast and flexible delivery options. This has led to the growth of express delivery services, which rely heavily on road freight transportation for timely deliveries.
The industry is currently facing challenges in the form of driver shortages, rising operational costs, supply chain disruptions, technology integration, and regulatory compliance. In essence, the industry is experiencing a significant shortage of qualified drivers, exacerbated by an aging workforce and high turnover rates. This shortage is impacting the ability to meet demand, driving up labor costs. Besides, rising operational costs in the form of increasing fuel prices, maintenance costs, and insurance premiums are adding financial pressure on service providers. Similarly, integrating advanced technologies into existing operations is challenging for service providers. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), in particular, struggle with the costs and complexities of adopting new technologies.
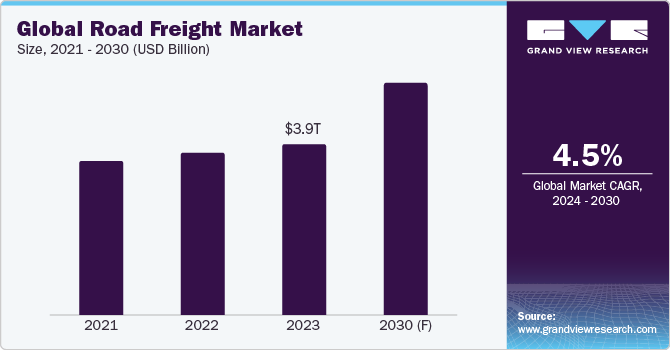
The global road freight market size was projected at USD 3,912 billion in 2023. In the time of the COVID-19 pandemic, this industry was severely affected by supply-chain disruptions. Road closures, movement restrictions, and government-imposed lockdowns led to several service providers temporarily stopping their services. Implementing safety protocols, such as regular sanitization, social distancing, and the use of personal protective equipment (PPE), added to the operational complexities. Moreover, health concerns and restrictions affected the availability of truck drivers and other logistics personnel. In the current scenario, the industry has adapted to the post-pandemic economic landscape, as service providers have managed to pass on the higher costs despite a sluggish market. Freight volumes, especially in sectors like agriculture and consumer goods, have seen significant improvement.
The key technological trends in this industry include the deployment of electric vehicles (EVs) and autonomous vehicles, the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), real-time freight visibility and automation, and predictive analytics. For instance, the industry is seeing a shift towards EVs and autonomous driving technologies. Electric trucks, including battery-electric and hydrogen fuel-cell electric vehicles, are becoming more prevalent as companies and governments push for lower emissions and cleaner energy sources.
Autonomous vehicles are reducing the cost of last-mile deliveries and improving efficiency in logistics. Service providers are leveraging AI and ML technologies to enhance shipment tracking, improve ETA accuracy, and optimize load planning. This not only improves operational efficiency but also enhances the customer experience by providing up-to-date information on shipments.
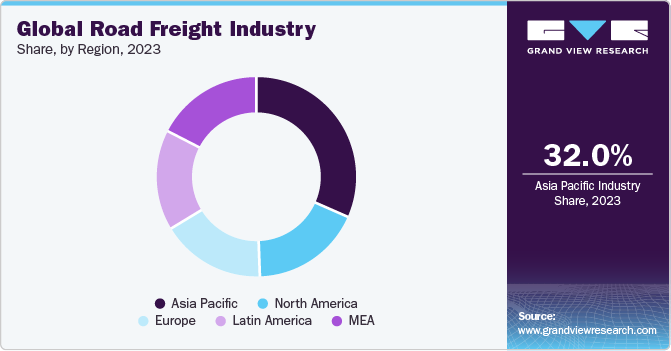
APAC dominates the global road freight industry, accounting for 32% of the global market share in 2023. The growth can be attributed to enhanced road infrastructure and increasing foreign investments. Additionally, the rapidly expanding e-commerce sector in developing countries, such as India and China, is significantly boosting the demand.
Supplier Intelligence
"What are the characteristics of the road freight market, and who are the key players involved?"
The global road freight industry is fragmented, with intense competition among key players. Prominent suppliers are emphasizing sustainability and eco-friendly practices, operational efficiency, customer service, and technological advancements. Suppliers are offering real-time tracking, faster delivery options, and flexible services to meet diverse customer needs. Moreover, they are using advanced analytics and artificial intelligence to optimize fleet usage, reduce operational costs, and improve service reliability.
Suppliers are focusing on reducing their carbon footprint through the adoption of green technologies and alternative fuels. Some of the key efforts include using renewable energy sources for EVs and exploring alternative fuels, including bio-LNG and bio-CNG. The goal is to achieve complete decarbonization and compliance with international climate agreements, such as the Paris Accord.
In terms of the demand landscape, buyers that are looking for the procurement of road freight are increasingly focusing on cost efficiency, service reliability, and performance. For instance, buyers may check service providers’ reliability, including on-time delivery rates and how they handle delays or disruptions. Additionally, buyers often seek references from other companies or look at online reviews to gauge the reputation of service providers.
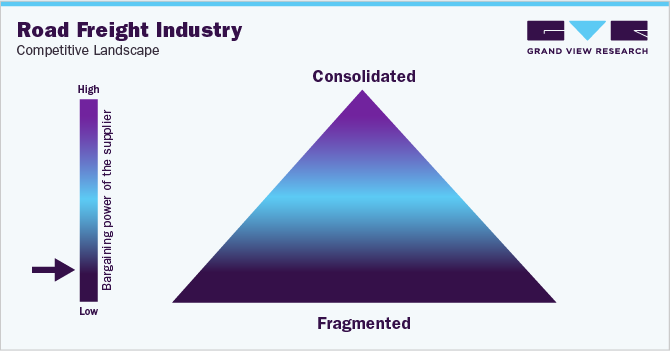
There are numerous medium-sized and small companies, with only a few large players operating in the industry. The leading service providers, such as DHL, FedEx, and UPS, along with others like J.B. Hunt, DSV, and Kuehne + Nagel, collectively hold a relatively small portion of the total market share. Buyers have significantly high negotiating capability due to the ease of switching suppliers. This increases pressure on suppliers to set competitive pricing rates while also preserving the service quality standards. Few key metrics that buyers can use to assess the performance of service providers include average delivery time, order accuracy, number of shipments, and freight cost per unit.
Prominent suppliers covered in the industry:
-
A.P. Møller - Mærsk A/S
-
C.H. Robinson Worldwide, Inc.
-
CMA CGM Group
-
DSV A/S
-
Expeditors International of Washington, Inc.
-
FedEx Corporation
-
J.B. Hunt Transport Services, Inc.
-
Knight-Swift Transportation Holdings Inc.
-
Kuehne + Nagel International AG
-
Landstar System Holdings, Inc.
-
Old Dominion Freight Line, Inc.
-
United Parcel Service of America, Inc.
Pricing and Cost Intelligence
“What are the main components of the cost structure for road freight, and what are the factors impacting the prices?"
For road freight procurement, buyers need to carefully consider several factors related to cost and pricing, which can help them achieve cost savings and manage budgets effectively. The cost structure contains the cost of vehicles, fuel, labor, technology, licensing and compliance, maintenance and repair, and other costs as the key components. Other costs include safety equipment, general and administrative, rent and utilities, loading and unloading, road taxes and tolls, and marketing and sales. Cost of vehicles and fuel account for the major components in the cost structure, followed by labor costs.
The accompanying chart showcases the cost structure. The breakdown of other costs may be influenced by various cost components, as depicted below:
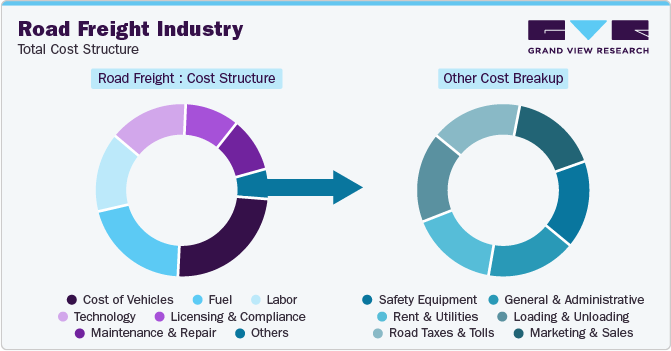
The prices of road freight services alter based on several circumstances, including type of shipment (FTL/LTL), speed and transit time, cargo volume and weight, distance covered, customs and tariffs, and labor cost. To illustrate, bulky and heavy shipments occupy more space on trucks or containers, leading to increased fuel consumption, longer driver hours, and greater wear and tear, all of which lead to a hike in overall prices. Specific macroeconomic factors that influenced the prices in 2024 were driver shortage, volatile fuel prices, trade policies, and geopolitical tensions.
FTL (Full Truckload) shipments often involve bulk commodities or large quantities of goods. Moreover, FTL shipments typically follow direct routes from the point of origin to the destination. These routes involve fewer stops, allowing trucks to cover longer distances efficiently. LTL (Less than Truckload) shipments, on the other hand, are frequently utilized for smaller loads. They involve multiple stops to pick up and deliver goods from various shippers. Each stop adds time and distance to the overall journey. FTL freights are generally priced higher than LTL, since the entire truck/vehicle is dedicated to a single shipment. LTL freights can, however, prove to be quite expensive if the load volumes are more than 10,000 pounds, and in such cases, using FTL is more suitable for buyers.
The average prices of FTL in the U.S. in 2024 (H1) were in the range of USD 2.10 to USD 2.50 per mile. During the same period, the prices in the U.K. spanned between USD 2.00 and USD 2.40 per mile, those in India spanned from USD 1.00 to USD 1.30 per mile, and those in Japan fell within USD 1.80 to USD 2.20 per mile. The average LTL prices in the U.S. during the same period (H1 2024) spanned within the range of USD 0.30 to USD 1.60 (measured per pound). The LTL prices in the U.K. fell within the range of USD 0.25 to USD 1.45 per pound. Those in India spanned within the spectrum of USD 0.20 to USD 1.15 per pound, and the Japanese LTL rates spanned from USD 0.25 to USD 1.50 per pound.
Key players in the road freight market deploy various pricing models. One of the key pricing models being used is flat-rate pricing. In this pricing structure, a fixed price is charged for a specific route or shipment regardless of weight, volume, or distance. It is often used for standardized routes or regular shipments where variables are consistent. Another key pricing model being deployed is mileage-based pricing, wherein the cost is calculated based on the distance traveled. This model charges a set rate per mile and is used for long-haul transportation, in which the primary cost driver is the distance covered. Other key pricing models are volume-based pricing, weight-based pricing, spot pricing, and contract pricing.
Sourcing Intelligence
“What methods do suppliers of road freight implement to engage with buyers? What type of engagement model is implemented?”
In terms of sourcing and procurement intelligence for road freight services, buyers commonly adopt an approved provider operating model for engaging with suppliers. By working with a pre-vetted list of providers, buyers ensure that reliable and competent service providers handle their logistics operations. Buyers have the flexibility to choose from multiple approved providers based on specific needs and circumstances while maintaining control over the selection process. Medium-term contracts (1 - 3 years) or long-term contracts (3 - 6 years) enable buyers to establish long-term relationships with service providers, which can lead to negotiated rates and cost savings over time.
"An approved provider is a vendor that matches a predefined set of selection criteria such as quality standards, prior-proven performances, qualifications, or others."
When it comes to engagement models, companies commonly outsource all of their transportation and logistics needs to a third-party logistics provider (3PL), by adopting a full-service outsourcing model. The 3PL handles everything from fleet management to route planning, warehousing, and delivery. 3PL providers usually have benefits such as lower shipping rates due to bulk buying and established relationships with carriers. Moreover, 3PLs have specialized knowledge and expertise in logistics, ensuring efficient management of supply chain activities. Companies can also easily scale operations on seasonal demand or market changes by partnering with 3PLs, thus offering added flexibility that in-house logistics may not easily achieve.
Buyers generally opt for local sourcing in this industry to improve supply chain-related and procurement costs. India and China are the preferred low-cost countries in Asia Pacific for sourcing. These countries have substantial cost benefits due to an abundance of resources such as vehicles and drivers, and robust road and highway infrastructure development. In Europe, Lithuania, Poland, and Bulgaria are cost-effective countries for sourcing these services due to lower fuel costs, cheaper labor costs, and favorable government policies.
The report also provides details regarding peer analysis, recent supplier developments, supply-demand analysis, competitive landscape, KPIs, SLAs, risk assessment, negotiation strategies, and low-cost/best-cost sourcing analysis. In this report, we have tried to provide a holistic industry perspective, an overview of the supplier landscape - the presence of different types of players and the competitive pressure within the industry as a whole (PORTER’s). Cost of vehicles forms the largest cost component of road freight. Similarly, the supply chain practices under sourcing and procurement are also covered. One such instance is the operating model that encompasses all the business processes conducted within an organization. It is an integral aspect of the company's operations and plays a crucial role in its success.
Road Freight Procurement Intelligence Report Scope
|
Report Attribute |
Details |
|
Growth Rate |
CAGR of 4.5% from 2024 to 2030 |
|
Base Year for Estimation |
2023 |
|
Pricing Growth Outlook |
5% - 10% increase (Annually) |
|
Pricing Models |
Flat-rate pricing, mileage-based pricing, volume-based pricing, weight-based pricing, spot pricing, contract pricing |
|
Supplier Selection Scope |
Cost and pricing, past engagements, productivity, geographical presence |
|
Supplier Selection Criteria |
Geographical service provision, industries served, years in service, employee strength, revenue generated, key clientele, regulatory certifications, freight type (FTL/LTL), maximum weight per shipment, containerized/non-containerized, long-haul/short-haul, temperature controlled, real-time tracking, value-add services (storage/labeling/bundling/packing), lead time, and others |
|
Report Coverage |
Revenue forecast, supplier ranking, supplier matrix, emerging technology, pricing models, cost structure, competitive landscape, growth factors, trends, engagement, and operating model |
|
Key Companies Profiled |
A.P. Møller - Mærsk A/S, C.H. Robinson Worldwide, Inc., CMA CGM Group, DSV A/S, Expeditors International of Washington, Inc., FedEx Corporation, J.B. Hunt Transport Services, Inc., Knight-Swift Transportation Holdings Inc., Kuehne + Nagel International AG, Landstar System Holdings, Inc., Old Dominion Freight Line, Inc., and United Parcel Service of America, Inc. |
|
Regional Scope |
Global |
|
Revenue Forecast in 2030 |
USD 5,323.7 billion |
|
Historical Data |
2021 - 2022 |
|
Quantitative Units |
Revenue in USD billion and CAGR from 2024 to 2030 |
|
Customization Scope |
Up to 48 hours of customization free with every report. |
|
Pricing and Purchase Options |
Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. Explore purchase options |
Frequently Asked Questions About This Report
b. The global road freight market size was estimated at approximately USD 3,912 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.5% from 2024 to 2030.
b. Increase in global trade activity, e-commerce expansion, rise in retail sales, improvement in transportation infrastructure, need for quicker deliveries, and growth of construction activities are driving the growth of this industry.
b. According to the LCC/BCC sourcing analysis, India, China, Lithuania, Poland, and Bulgaria are the cost-effective countries in their respective regions for sourcing road freight services.
b. This industry displays a fragmented landscape, with an intense level of competition. Some of the key players are A.P. Møller – Mærsk A/S, C.H. Robinson Worldwide, Inc., CMA CGM Group, DSV A/S, Expeditors International of Washington, Inc., FedEx Corporation, J.B. Hunt Transport Services, Inc., Knight-Swift Transportation Holdings Inc., Kuehne + Nagel International AG, Landstar System Holdings, Inc., Old Dominion Freight Line, Inc., and United Parcel Service of America, Inc.
b. Cost of vehicles, fuel, labor, technology, licensing & compliance, maintenance & repair, and others are the major cost components in road freight services. Other costs include safety equipment, general & administrative, rent & utilities, loading & unloading, road taxes & tolls, and marketing & sales.
b. In road freight procurement, the best practices for selecting suppliers include comparing the prices quoted by service providers, assessing geographical service capabilities, checking years of experience, comparing client testimonials, evaluating lead time, checking sustainability initiatives, and assessing level of technological adoption.
Add-on Services
Should Cost Analysis
Component wise cost break down for better negotiation for the client, highlights the key cost drivers in the market with future price fluctuation for different materials (e.g.: steel, aluminum, etc.) used in the production process
Rate Benchmarking
Offering cost transparency for different products / services procured by the client. A typical report involves 2-3 case scenarios helping clients to select the best suited engagement with the supplier
Salary Benchmarking
Determining and forecasting salaries for specific skill set labor to make decision on outsourcing vs in-house.
Supplier Newsletter
A typical newsletter study by capturing latest information for specific suppliers related to: M&As, technological innovations, expansion, litigations, bankruptcy etc.