- Home
- »
- Renewable Chemicals
- »
-
Biopolymers Market Size, Share And Growth Report, 2030GVR Report cover
![Biopolymers Market Size, Share & Trends Report]()
Biopolymers Market (2025 - 2030) Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report By Product (Bio-PE, Bio-PET), By End-use (Packaging, Consumer Goods), By Application, By Region, And Segment Forecasts
- Report ID: GVR-4-68040-160-8
- Number of Report Pages: 150
- Format: PDF
- Historical Range: 2018 - 2022
- Forecast Period: 2025 - 2030
- Industry: Specialty & Chemicals
- Report Summary
- Table of Contents
- Segmentation
- Methodology
- Download FREE Sample
-
Download Sample Report
Biopolymers Market Summary
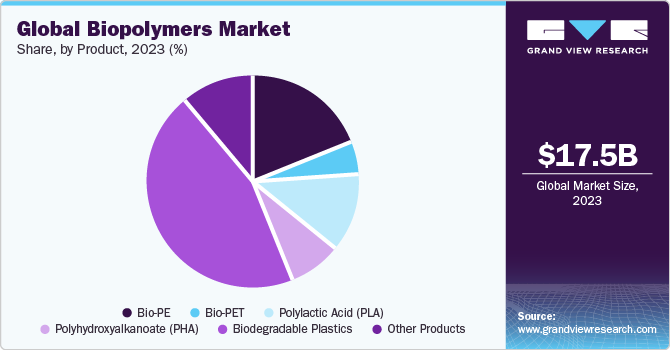
The global biopolymers market size was estimated at USD 20.98 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 50.17 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 15.6% from 2024 to 2030. This is majorly attributed to the expanding demand for PHA-based environmental plastics.
Key Market Trends & Insights
- Asia Pacific region accounted for the largest revenue share of around 37.25% in 2023.
- The biopolymers market in China is expected to grow at a significant CAGR over the forecast period.
- Based on end-use, the packaging segment accounted for the largest share of 38.58% in 2023.
- Based on application, the bottle segment accounted for the largest share of 31.05% in 2023.
- Based on product, the biodegradable polyesters segment accounted for the largest share of 45.03% in 2023.
Market Size & Forecast
- 2024 Market Size: USD 20.98 Million
- 2030 Projected Market Size: USD 50.17 Million
- CAGR (2024-2030): 15.6%
- Asia Pacific: Largest market in 2023
Corresponding to the heightened demand for eco-friendly packaging from an extensive variety of end-use areas, major packaging and plastics manufacturing companies are shifting to biodegradable products. Biopolymers are engaged in an array of end-use applications, including biomedical, pharmaceuticals, and food. Because of their excellent recovery characteristics, they are in tremendous demand in biomedical applications, as they assist in the treatment of wounds of all shapes and sizes.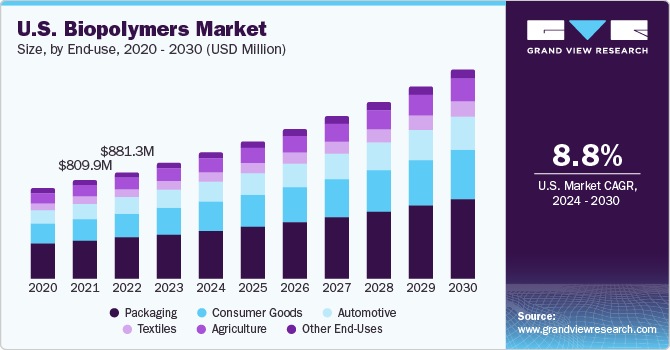
According to the Ellen MacArthur Foundation (EMF), 78 million tons of single-use plastic packaging is manufactured yearly- of which under 2% is successfully recycled. Staggeringly, 32% of this product is poured out into the natural environment, as a result of insufficient processing and waste collection infrastructure. Given this realism, policymakers, manufacturing companies, and brands globally are examining techniques to remove the destructive pollution triggered by leakage and to improve recycling rates. Thus, there has been an enormous endeavor to foster packaging that can be recycled in numerous end-of-life environments. As a result, the demand for the product is subjected to strengthen rapidly.
Biopolymers are polymeric products derived from raw materials like sugarcane, and corn, as well as residual wood and standing timber. Biopolymers are biodegradable, in contrast to the conventional polymers or plastics, which results in global warming and pollution. The surge in perception of the usage of bio-based polymers is predicted. As a result, biopolymers are regarded as a more sustainable replacement to traditionally used petroleum-based plastics, because they can be broken down by natural methods and do not pose a risk to the ecosystem.
Customers are becoming extra sensible about their carbon footprint and are asking for more eco-friendly products. Administrations around the globe are also taking measures to decrease plastic waste by enforcing sanctions on single-use plastics and advocating the use of natural packaging solutions. This inclination is expected to continue over the forecasted period, as businesses and consumers become more responsive to the impact that conventional petrochemical-based plastics have on the ecosystem.
On the other hand, the elevated cost of manufacturing biopolymers is predicted to restrict market growth. Biopolymers are more expensive than conventional petroleum-based plastics. Bio-based ethylene, for instance, is more costly than petroleum-based ethylene. Regardless of strengthening customer pressure for renewable products as well as government regulation/ guidelines on the utilization of virgin plastics, the expansion of the biopolymer sector is being ‘held back’ by differences in product quality and costs.
End-use Insights
The packaging segment accounted for the largest revenue share of around 38.58% in 2023. The demand for biopolymers in packaging is increasing for several reasons, driven by environmental, regulatory, and consumer-driven factors. Biopolymers are often derived from renewable resources such as plants or bacteria, making them a more sustainable alternative to traditional petroleum-based plastics. The environmental impact of traditional plastics, particularly in terms of pollution and long degradation times, has led to increased interest in eco-friendly alternatives.
Biopolymers are gaining traction in consumer goods for diverse reasons, mirroring a broader shift towards sustainability and environmental accountability in the consumer product sector. Governments and regulatory bodies across different regions are instituting measures to diminish plastic waste and endorse the utilization of more sustainable materials. This has established a regulatory landscape fostering the integration of the product into consumer goods.
In the automotive sector, biopolymers can be engineered to have favorable strength-to-weight ratios. By replacing traditional materials with lightweight biopolymers, vehicles can achieve weight reduction, contributing to improved fuel efficiency and reduced carbon emissions. In addition, advances in material science have led to the development of biopolymers with enhanced mechanical properties, durability, and heat resistance. These innovations make them more suitable for a wider range of automotive applications.
Application Insights
The bottle segment accounted for the largest revenue share of around 31.05% in 2023. This is attributable to the shift in the consumption trends regarding renewable/bio-based plastics. Biopolymers like PLA are being used increasingly in the manufacturing of bottles due to their eco-friendly nature.
In the medical sector, due to their biocompatibility, biopolymers are being extensively used. In addition, some biopolymers can be designed to biodegrade over time, eliminating the need for a second surgery to remove the implants. This property is beneficial where controlled drug release or temporary support is required. To sum up, the use of biopolymers is in alignment with the growing emphasis on materials that are eco-friendly, effective, and safe.
Biopolymers are often biocompatible, meaning they are well-tolerated by plant tissues. This compatibility can enhance the interaction between the coating and the seed, promoting successful germination and seeding development. Moreover, some biopolymers can be engineered to carry and release bioactive molecules and nutrients. These controlled release methods can provide essential elements to germinating seeds, thus supporting their initial growth rate.
Product Insights
The biodegradable polyesters segment accounted for the largest revenue share of around 45.03% in 2023. This is attributed to environmental concerns and a growing emphasis on sustainable and eco-friendly practices in numerous end-use industries. In addition, biodegradable polyesters provide a solution to the end-of-life challenges associated with traditional plastics. Products made from biodegradable polyesters can be designed to break down naturally, reducing the need for long-term disposal and contributing to a circular economy.
Bio-polyethylene (Bio-PE) production typically results in lower greenhouse gas emissions when compared to traditional polyethylene. The cultivation of plants for feedstock absorbs CO2 from the atmosphere, contributing to a more favorable carbon footprint. Further, ongoing technological advancements have improved the production processes and properties of bio-PE, making it more viable for a boarder range of application areas.
Polylactic Acid (PLA) is a bio-based polymer, meaning it is not derived from fossil fuels. This reduces the dependency on non-renewable resources and aligns with the global shift towards sustainable and eco-friendly products. PLA has versatile properties due to which it is suitable for various applications like packaging, disposable tableware, biomedical devices, and textiles. Its adaptability contributes to its increasing demand across various end-use industries.
Regional Insights
Asia Pacific region accounted for the largest revenue share of around 37.25% in 2023. The region has abundant agricultural resources that can be used as feedstocks for the production of biopolymers. For example, sugarcane and corn, common raw materials for bio-based polymers/ plastics, are grown in significant quantities in this region, providing a sustainable source for the production of biopolymers.
Europe has been at the forefront of promoting a circular economy aiming to reduce waste and encourage recycling. Biopolymers, especially those that are biodegradable or compostable, align with these initiatives by offering sustainable alternatives to traditional plastics. In addition, the packaging industry in Europe has been actively adopting biopolymers to meet sustainability goals and address concerns related to single-use plastics. Biodegradable and bio-based packaging materials, including biopolymer alternatives, are gaining traction.
There have been significant investments in North America in the production and development of biopolymers. This includes investment in research and development, new manufacturing facilities, and partnerships between companies to advance biopolymer technologies. In addition, while not as stringent as European regulations, North America has seen developments in regulations and guidelines promoting sustainable practices. These include measures at the state and federal levels aimed at reducing plastic waste and encouraging the use of biodegradable and bio-based materials.
Key Companies & Market Share Insights
The development of cost-effective biopolymers is one of the major strategies undertaken by numerous manufacturing companies around the globe. In addition, major manufacturers dominate the market with various strategy initiatives such as product launches, expansion, mergers & acquisitions, and certifications for their products. For instance, in April 2023, NatureWorks introduced the latest ‘Ingeo’ biopolymer solution for increased strength and softness in biobased nonwovens for hygiene applications.
Key Biopolymers Companies:
- Biopolymer Industries
- BASF SE
- Solanyl Biopolymers
- BioPolymer GmbH & Co. KG
- Ecovia Renewables Inc.
- BiologiQ, Inc.
- ADM
- DuPont
- Novamont
- BIOTEC
Biopolymers Market Report Scope
Report Attribute
Details
Market size value in 2025
USD 24.25 billion
Revenue forecast in 2030
USD 50.17 billion
Growth rate
CAGR of 15.6% from 2025 to 2030
Base year for estimation
2024
Historical data
2018 - 2022
Forecast period
2025 - 2030
Quantitative units
Volume in kilotons, revenue in USD million/billion, and CAGR from 2025 to 2030
Report coverage
Kilotons in volume, revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends
Segments covered
Product, application, end-use, region
Regional scope
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Central & South America; Middle East & Africa
Country scope
U.S.; Canada; Mexico; Germany; UK; France; Italy; Spain; Netherlands; China; India; Japan; South Korea; Australia; Brazil; Argentina; Saudi Arabia; South Africa
Key companies profiled
Biopolymer Industries; BASF SE; Solanyl Biopolymers; BioPolymer GmbH & Co. KG; Ecovia Renewables Inc.; BiologiQ, Inc.; ADM; DuPont; Novamont; BIOTEC
Customization scope
Free report customization (equivalent up to 8 analysts’ working days) with purchase. Addition or alteration to country, regional & segment scope.
Pricing and purchase options
Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. Explore purchase options
Global Biopolymers Market Report Segmentation
This report forecasts revenue & volume growth at global, regional, and country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2018 to 2030. For this study, Grand View Research has segmented the global biopolymers market report based on product, application, end-use, and region:
-
Product Outlook (Volume, Kilotons; Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
-
Polysaccharides
-
Cellulose Acetate
-
Others
-
-
Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA)
-
Polylactic Acid (PLA)
-
Polybutylene Succinate (PBS)
-
Bio-based Polyethylene (Bio-PE)
-
Bio-based Polyethylene Terephthalate (Bio-PET)
-
Others
-
-
Applications Outlook (Volume, Kilotons; Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
-
Films
-
Bottle
-
Fibers
-
Seed Coating
-
Vehicle Components
-
Medical Implants
-
Other Applications
-
-
End-use Outlook (Volume, Kilotons; Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
-
Packaging
-
Consumer Goods
-
Automotive
-
Textiles
-
Agriculture
-
Other End-Uses
-
-
Region Outlook (Volume, Kilotons; Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
-
North America
-
U.S.
-
Canada
-
Mexico
-
-
Europe
-
Germany
-
UK
-
France
-
Italy
-
Spain
-
-
Asia Pacific
-
China
-
India
-
Japan
-
South Korea
-
-
Central & South America
-
Brazil
-
Argentina
-
-
Middle East & Africa
-
Saudi Arabia
-
South Africa
-
-
Frequently Asked Questions About This Report
b. The global biopolymers market size was estimated at USD 17.54 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 19.37 billion in 2024.
b. The global biopolymers market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.4% from 2024 to reach USD 38.69 billion in 2030.
b. Asia Pacific dominated the global biopolymers market with a revenue share of 37.25% in 2023. The region has abundant agricultural resources that can be used as feedstocks for the production of biopolymers. For example, sugarcane and corn, common raw materials for bio-based polymers/ plastics, are grown in significant quantities in this region, providing a sustainable source for the production of biopolymer.
b. Some of the key players in the global biopolymers market include BASF SE, ADM, BIOTEC, DuPont, Novamont, and Biopolymer Industries, among others.
b. Biopolymers are polymeric products derived from raw materials like sugarcane, and corn, as well as residual wood and standing timber. The surge in perception of the usage of bio-based polymers is predicted. As a result, biopolymers are regarded as a more sustainable replacement to traditionally used petroleum-based plastics, because they can be broken down by natural methods and do not pose a risk to the ecosystem.
Share this report with your colleague or friend.
Need a Tailored Report?
Customize this report to your needs — add regions, segments, or data points, with 20% free customization.

ISO 9001:2015 & 27001:2022 Certified
We are GDPR and CCPA compliant! Your transaction & personal information is safe and secure. For more details, please read our privacy policy.
Trusted market insights - try a free sample
See how our reports are structured and why industry leaders rely on Grand View Research. Get a free sample or ask us to tailor this report to your needs.