Cybersecurity is becoming the new mandate to ensure a safe and secure supply chain
Overview
The supply chain sector includes a complex and interconnected network of companies that may be prone to cyber threats. Since these networks are interconnected and interdependent and are used for delivering goods and services to consumers/end users, a cyber-attack can cause a ripple effect across the entire network, finances, and company operations. Risk management leaders and audit executives in 2023 have ranked cybersecurity as the top risk category. The implementation of strong cybersecurity protections has, thus, become a critical step in businesses’ strategies. In 2023, more than 86% of top C-suite leaders have not only prioritized but also made significant cybersecurity initiatives for one key business sector. All these have, in turn, pushed companies to increase their budgets. Industry experts estimate that in 2024, budgets for data security will increase between 12 – 15% over 2023. Accenture’s 2023 survey report [consisting of 3,000 respondents (2,500 security officials, and 500 CEO – CFO – C suite leaders) across 14 countries from 15+ industries.] indicates that 40% of companies employed third-party or managed service providers to handle cybersecurity operations and overcome skill shortages.

More devices are now connected to the internet and business networks than ever before. The dependence on IT has increased significantly due to digital transformation projects. In nearly all parts of the world, cybercrime continues to increase. The major types of cybercrime include – malware, phishing, and ransomware. In 2023, almost 97% of companies witnessed an increase in cybercrimes since the Russian-Ukraine war tensions. 39% of organizations have started working closely with government agencies to address such issues through policies or recommendations. 54% of companies feel that most of the third-party service providers and/or networks external to their firms are more prone to attacks. The percentage of successful intrusions from outside the company remains high at 61% in 2023. Supply chain partner threats are proportionately higher in certain industries, such as utilities, at 62% in 2023.
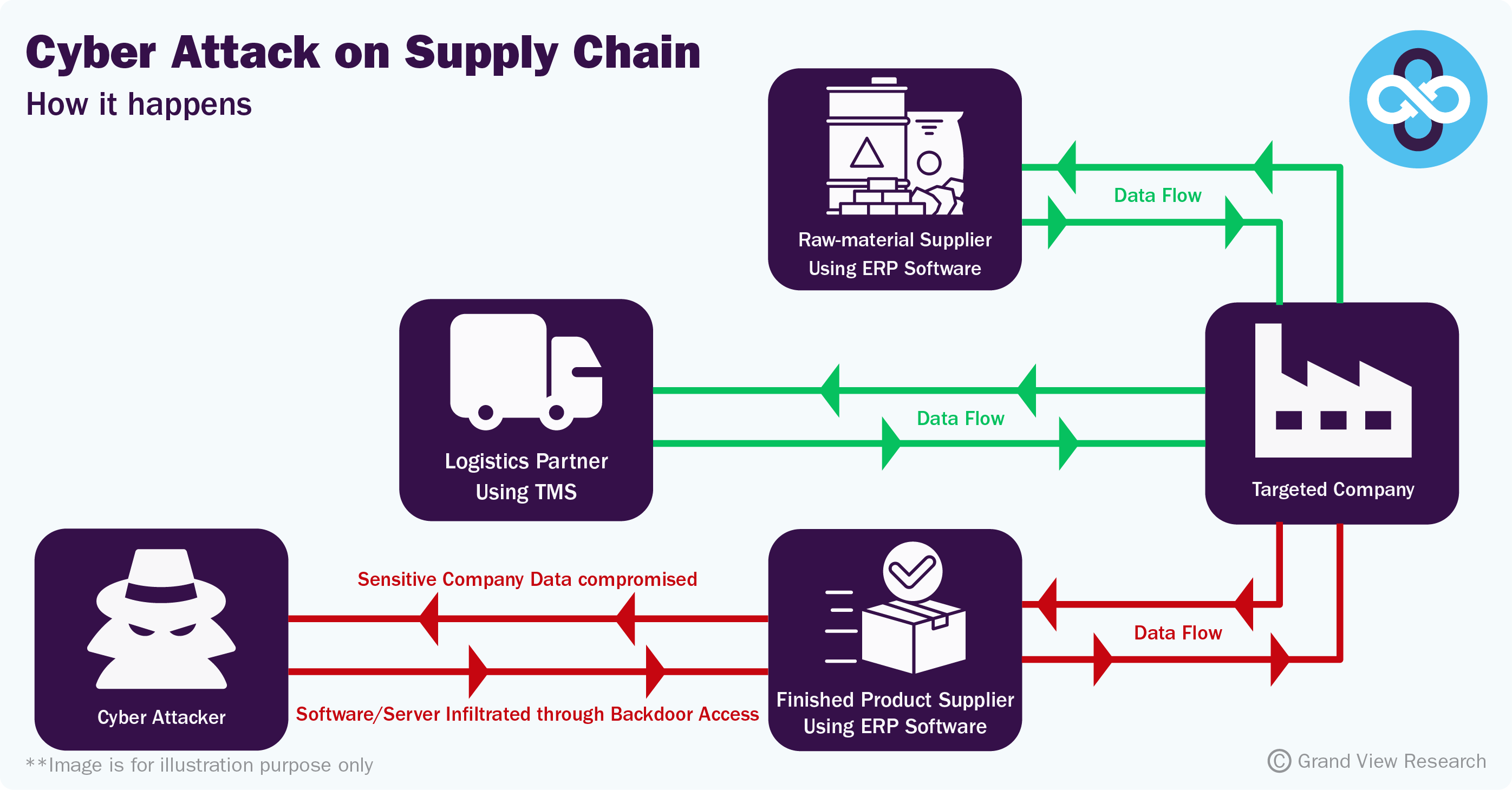
In the last six months of 2023, the world has witnessed a spike in supply chain cybercrimes. When cybercriminals target a weaker link in a company's supply chain, they are considered supply chain attacks, making cyber security procurement a paramount requirement for organizations across the globe. An example of this might be a customer, vendor, supplier, or third-party software library that the company relies on.
Some Recent Supply Chain Cyber-attack Instances
November/December 2023: JetBrains Supply Chain Attack:
Overview - JetBrains’ TeamCity is a commercial software that enables companies to build intelligent tools on its continuous integration/continuous delivery (CI/CD) servers. Some of the leading companies that use TeamCity include P&G, Google, Microsoft, Volkswagen, HP, and X. Many companies in the sourcing/procurement industry use this tool to test, build, and compile their software in an automated manner.
Incident - The organization (Russian Gang – CozyBear) that carried out the infamous SunBurst assault on SolarWinds in 2020 and the BianLian ransomware gang are actively exploiting a vulnerability in JetBrains TeamCity’s software. The recent vulnerabilities are being tracked as CVE-2024-27198 and CVE-2024-27199 having CVSS scores of 9.8 and 7.3, respectively. Unauthenticated criminals can gain administrator access using remote code execution, which eliminates the need for user interaction. Many code bases, CI/CD pipelines, and any saved credentials on the TeamCity servers are at significant risk and can be used for exploitation due to these vulnerabilities. This can pose a serious supply chain risk.
Impact on the supply chain - This attack exposed more than 3,000 on-premises servers and impacted 30,000 JetBrains customers. The susceptible hosts are mostly found in the U.S., Germany, Russia, the Netherlands, China (a few), and France. The supply chain networks of vendor companies are at a high risk as the attackers try to gain full control of the servers. Software supply chain vulnerabilities will negatively impact the companies in the supply chain operations. This is because they depend on vulnerable components that play a critical role in their ecosystems/operations.
October 2023: Okta Supply Chain Attack:
Overview - Okta is an identity and access management (IAM) company in the U.S. Companies in the supply chain/ procurement industry use this tool or cloud platform to gain unified access to multiple partner portals, streamline lifecycle management, and improve reporting and visibility to maintain security and compliance. Okta’s software is used by some of the leading companies, such as Microsoft, Takeda Pharmaceuticals, and FedEx, thus making it a common target for criminals.
Incident – The company's support system was hacked when an Okta employee logged into his/her personal Google account while using a company-owned laptop. The hackers (Scattered Spider gang) behind the assault retrieved a report including the names and email addresses of all clients that utilize Okta’s customer care system. It was reported that the criminals had launched their attack using HTTP Archive (HAR) files, which allowed support personnel to diagnose technical problems by emulating browser actions. The company’s customer system and 200 clients’ data were affected as a result of the data breach. Okta also suffered four significant cybercrimes in 2022. The most notable is the one caused by “Lapsus$” (hacking gang), which posted pictures of breached systems to Telegram.
Impact on supply chain - Okta’s compromised supply chain systems helped hackers gain access to the networks of its vendors. Cloudflare and Atlassian servers were negatively impacted as a result of stolen credentials. Procurement leaders using Atlassian’s Jira tool are also at risk of exposure due to this breach. Security measures are being strengthened by companies operating in this supply chain space. There is an increased use of risk monitoring platforms by the affected clients or end users that provide them with full visibility of the ecosystem’s attack surface in real time.
Some other examples include the MOVEit supply chain attack in June 2023, the 3CX supply chain attack in late March/April 2023, and the Applied Materials supply chain attack, which cost the company USD 250 million due to ransomware.
According to the IBM 2023 report, the cost of data breaches amounted to USD 4 – 5 million among 553 companies between March 2022 and 2023. On average, in 2023, it was also found that the average cost of a successful ransomware attack was between USD 1 – 1.6 million. In contrast, the recovery cost for companies was around USD 1.8 – 2 million. These recovery costs included the time of people or employees, downtime, costs of multiple devices, and many lost opportunities in businesses.
Supply chain executives or procurement leaders, as a result of these attacks, in recent times, have considered it imperative to implement modern tools that can surpass the limitations of traditional application security testing methodologies. It is critical for both developers and software users to properly inspect the compiled binary before deployment. All development environments must take measures to prevent any malicious code from being inserted into the codebase. This includes secure coding repositories, deployment of highly secure coding workstations, code signing, and frequent code review.
Companies operating in the supply chain segment are implementing a strong vendor risk management framework for preventing supply chain assaults. In addition to having a thorough patch management policy, procurement leaders are prioritizing patching depending on its criticality and possible influence on business operations. The organizations are verifying the strength and robustness of their supply chain software by conducting penetration tests or carrying out adversary simulation exercises. Some of the other strategies include – the implementation of honeytokens, secure privileged access management, external and internal PAM defenses, a zero-trust architecture (ZTA), and strict shadow IT rules. As of January 2024, it is estimated that 27.7% of organizations are affected by a data breach, of which almost 60% are the result of a third party's action. It will, therefore, be possible to reduce overall incidents of data breaches if the companies concentrate on mitigating third-party breaches that occur during the supply chain process.
Pipeline Suggests Following Measures to Mitigate the risk of Cyber-attacks
To avoid the possibility of a cyber-attack, organizations now have no choice but to adopt proactive cybersecurity risk mitigation strategies. Risk mitigation consists of three components – prevention, detection, and remediation. A few methods listed below can help to reduce the risks of attacks on an organization's IT infrastructure.
Continuous upgrades and updates in software: It is highly recommended to apply all software updates as soon as they become available. Ideally, companies should automate this process to ensure timely installation. Cybercriminals are quick to exploit vulnerabilities in software, so it is important to stay up to date with the latest patches. Companies should use updates delivered through protected links and test them prior to releasing them into production.
Limited and privileged access to accounts: It is highly recommended that companies begin their program with a zero-trust framework, as account credentials can be obtained by threat actors. This model entails assigning account privileges only when users need them, and not over-assigning them. To securely reset credentials, it is important to develop documented procedures or use a privileged access management tool to automate the process.
Ensure that software execution policies are signed.
Utilize defenses that are application-aware to segment networks.
Implement multi-factor authentication.
Continually monitor and evaluate the cybersecurity plans of third parties.
Access our report or request for a free sample of the study titled “Cyber Security Procurement Intelligence Report, 2023 - 2030 (Revenue Forecast, Supplier Ranking & Matrix, Emerging Technologies, Pricing Models, Cost Structure, Engagement & Operating Model, Competitive Landscape)” to gain more insights into Cybersecurity Procurement Practices, Supplier Ranking & Selection Procedures and Benchmarks for this category.
