- Home
- »
- Market Trend Reports
- »
-
Pricing Model Analysis For Healthcare Contract Research Organizations
Report Overview
The growing number of clinical trials across the globe in past few years has significantly increased the overall clinical trial costs. High clinical cost of clinical trial is owing to complexity of novel therapies such as personalized medicine and cell & gene therapy, and stringent regulatory requirements. Thus, surge in the cost of clinical trials leads to higher expenses in operational logistics, patient recruitment, and regulatory compliance. Thus, Pharmaceutical and medical device companies are increasingly outsourcing clinical research activities to Contract Research Organizations (CROs) for cost-effective solutions to stay competitive & flexible in the world of growing knowledge, gradually sophisticated technologies, and unstable economic environment.
Several CROs offers specialized knowledge, advanced technologies, and geographical reach, allowing pharmaceutical companies to streamline clinical trials and reduce overheads. Furthermore, increasing demand for personalized medicine, stringent regulatory requirements requiring extensive documentation and compliance efforts, and the need for accelerated time-to-market are another key aspects contributing to the enhanced utilization of CROs in the clinical trial landscape.
As per the data published by the Sofpromed, in the U.S., the clinical trial cost for phase I, II, and III are in the range of USD 1.4 million to USD 6.6 million, USD 7.0 million to USD 19.6 million and USD 11.5 million to USD 52.9 million, respectively. As early phase clinical trials often involving thorough safety and dosage studies, require significant investment in advanced technologies and patient monitoring, thereby accelerating trial costs. Whereas late-phase trials with larger patient populations and extended durations increase further financial burdens. Therapeutic areas such as oncology and rare diseases, which mandate specialized protocols and targeted patient recruitment, also contribute to higher expenses. For instance, the clinical trial cost structure for key therapeutic area by each phase are as mentioned below:
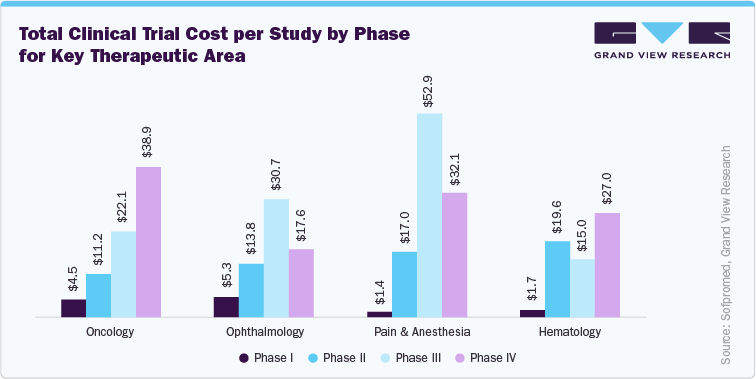
As a result, CROs are modifying their pricing models to exhibit these accelerating costs, incorporating several factors such as process complexity, trial timeframe, and therapeutic specialization to ensure financial sustainability and competitive service offerings.
Cost Structure Analysis, By Key Cost Components
Healthcare CRO’s service cost structure includes significant direct and indirect costs incurred during overall operations. Direct costs include expenses that are directly associated with conducting clinical trials, such as regulatory affairs, site management, clinical monitoring, project management, personnel salaries, clinical supplies, patient recruitment and retention costs. These costs are directly correlating with the execution of specific clinical trial and can vary depending on the therapeutic area, phase, and drug complexity.
On the other hand, indirect costs include overhead expenses such as administrative salaries, office rent, utilities, technology and infrastructure investments, and staff training. Indirect costs are necessary to maintain the operational framework and support core functionalities of the CRO.These costs are fundamental for financial planning and pricing strategies to make sure that CROs remain competitive in the market.
Factors Influencing Direct And Indirect Cost Components
Several factors influence the direct and indirect cost components of healthcare CROs. Direct costs are heavily influenced by the complexity and duration of clinical trials, type of therapeutic area, and the geographic presence of trial sites. For instance, clinical trials in oncology or rare diseases typically incur higher direct costs owing to specialized protocols and patient recruitment challenges. Further, indirect costs are affected by numerous factors such as the scale of the operations, the level of investment in technology and infrastructure, and the regulatory landscape.
Stringent regulatory requirements and the need for robust data management systems stimulate indirect costs as several CROs proactively invest in compliance and advanced IT solutions to enhance data integrity and security. Balancing these costs is essential for maintaining competitive service offerings and financial health. Several CROs strategically manage and optimize both cost components to deliver high-quality services while remaining financially stable in the fierce competition.
Clinical Trial Cost Framework In Asia Pacific
The cost structure of clinical trials in the Asia Pacific region is influenced by a combination of lower operational costs and increasing infrastructure investments. Direct costs, such as personnel salaries, patient recruitment, and site management fees, are commonly lesser in APAC as compared to Western regions due to lower labor and operational costs. Further, presence of large and diverse patient population, which accelerate patient recruitment and reduce associated costs, the study of numerous diseases, and providing a more comprehensive understanding of drug efficacy across different demographics is another factor boosting regional demand.
Indirect costs, including administrative expenses and regulatory compliance are also more economical, though they are rising as countries in the region strengthen their regulatory frameworks and invest in advanced clinical trial infrastructure. The improving regulatory environment and increasing investments in clinical trial infrastructure further enhance the attractiveness of the regional market. Governments in numerous APAC countries are also offering incentives to boost local clinical trial capabilities, making the region a preferred destination for global clinical trials.
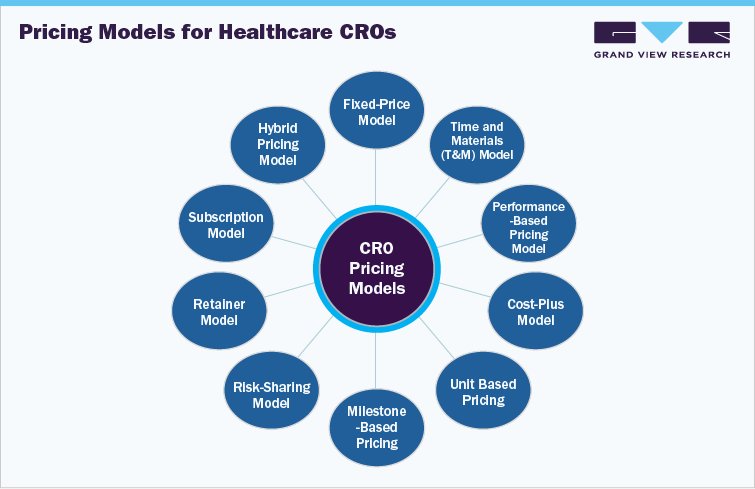
The fixed pricing model is commonly used pricing structure in the healthcare CRO industry. The fixed pricing model involves a pre-determined cost for a specific project or phase, providing clients with cost certainty and simplified budgeting. This model benefits clients by offering predictable expenses and reducing financial risk, especially for well-defined projects. However, CROs must carefully estimate the scope and resources required to avoid under-pricing and potential losses.
Further, in recent years, innovative approaches to pricing CRO services are transforming fee structures, with enhanced flexibility, goal alignment, and risk-sharing. Key strategies include risk-based pricing, in which CROs and sponsors share financial risks by securing compensation to successful milestones, and value-based pricing, in which fees imposed based on the value delivered, such as faster time-to-market or improved patient recruitment rates.
Moreover, subscription models provide predictable costs and constant service availability, promoting long-term partnerships. Hybrid models combine several pricing components that offer flexibility and risk mitigation for diverse project complexities. These modern approaches are increasingly adopted by numerous service providers to strengthen client relationships, improve project outcomes, and ensure financial sustainability.
Share this report with your colleague or friend.
GET A FREE SAMPLE
This FREE sample includes market data points, ranging from trend analyses to market estimates & forecasts. See for yourself.
![gvr icn]()
NEED A CUSTOM REPORT?
We can customize every report - free of charge - including purchasing stand-alone sections or country-level reports, as well as offer affordable discounts for start-ups & universities.
Contact us now to get our best pricing.
![esomar icon]()
ESOMAR certified & member
![ISO]()
ISO Certified
We are GDPR and CCPA compliant! Your transaction & personal information is safe and secure. For more details, please read our privacy policy.
We are committed towards customer satisfaction, and quality service.
Client Testimonials

"The quality of research they have done for us has been excellent..."
ISO Certified


