Telecom Cloud Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report By Component (Solution, Services), By Deployment Type, By Service Model, By Application, By Enterprise Size, By Region, And Segment Forecasts, 2022 - 2030
- Report ID: GVR-4-68039-968-0
- Number of Report Pages: 120
- Format: PDF
- Historical Range: 2017 - 2020
- Forecast Period: 2022 - 2030
- Industry: Technology
Report Overview
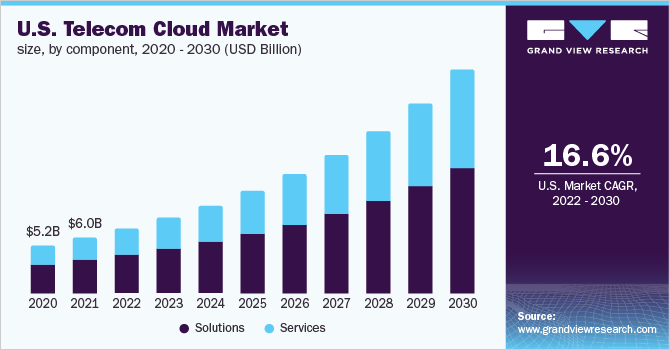
The global telecom cloud market size was valued at USD 20.4 billion in 2021 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 19.9% from 2022 to 2030. The telecommunication cloud is a next-generation network architecture that integrates software-defined networking, network function virtualization, and cloud-native technologies into a distributed computing network. Automation and orchestration are essential since the network and computing resources are scattered across locations and clouds. This progression is called the implementation of virtualized and programmable network infrastructure that uses automation and artificial intelligence. It also includes adopting novel cloud business strategies that alter network infrastructure. The rapid digital transformation between industries increased significant data consumption, and increased internet & mobile device penetration are some of the global telecom cloud trends.
It is most commonly used in the telecom business and is referred to as multi-cloud computing. It refers to the shift of Communications Service Providers (CSPs) from vertically integrated proprietary hardware-based infrastructure networks to cloud-based technologies. This change eliminates the technological constraints that are now impeding CSP expansion.
Finally, this transition enables the agility, performance, and scalability required to succeed in the digital world. CSP modernization allows future-ready networks to handle current and futuristic applications. The primary business advantages are increased customer satisfaction, corporate agility, cost savings, and others. The usage of standard computational hardware and automation reduces CapEx and OpEx, which also drives the adoption of cloud computing in the telecommunication industry.
It also delivers innovative bespoke B2B solutions, such as CSP may bring highly customized corporate products to market rapidly and affordably. It makes it simple to collaborate with business service partners by providing access to public cloud services from any device, at any time. Additionally, it protects your consumers and profits from competitors; for instance, it enables operators to swiftly alter business models to test new goods, services, and pricing schemes.
It also makes setting up new consumer experiences and communication channels easier. Furthermore, the lower CapEX and OPEX needs of the telecommunication industry, better service resilience, and capacity to respond swiftly to faults and demand changes allow operators to maintain service levels and competitive pricing. These advantages result in lower client attrition.
COVID-19 Impact Analysis
The global communications industry was affected by the worldwide pandemic outbreak and the subsequent chain of lockdowns. Telecom networks saw massive traffic during this period, and the need for more telecom capacity was at an all-time high. With the COVID-19 pandemic's aftereffects, the worldwide telecom sector was revolutionizing technologically to meet its users' increased expectations better.
The adoption of next-generation communication technologies, such as 5G network installations, was accelerated in many regions of the world and prioritized service automation. According to a survey issued by Nokia, more than 64% of communication service providers concentrated on enhancing operational service automation with cloud technology. During this time, these dynamics aided the growth of the industry.
The telecom Sector is expected to benefit from the COVID-19 problem but must demonstrate its resilience. For example, digital media behemoths like Netflix and YouTube have reduced the quality of their material streaming to prevent network congestion during global lockdowns. This might lead to more significant investments in existing network infrastructure and the impending 5G network, which would help to create employment.
Many broadcasters have suffered a reduction in ad income, which may continue until economies completely recover. Furthermore, factors such as an anticipated increase in remote work, remote training, and digital entertainment combined with a trend toward small and efficient manufacturing would provide lucrative opportunities for the market.
Component Insights
The component segment is bifurcated into solutions and services. Among these, the solution segment dominated with a revenue share of 60.2% in the year 2021. The solution segment offers unified communication and collaboration, content delivery networks, Network function virtualization, and other solutions.
The rising internet and mobile device penetration are driving the adoption of solutions. As a result, organizations are increasingly experiencing the need to leverage new technology to boost company agility and operational efficiencies. Telephone, email, voice mail, IM (instant messaging) and presence, unified messaging, audio, web, and video conferencing, file sharing and white-boarding, social networking, mobility, and other applications are being deployed by enterprises.
Furthermore, the exponentially expanding media content and demand for rich video content among increasing internet users and the digitalization trend among enterprises across end-user sectors drive the demand for content delivery network solutions.
The services segment is anticipated to witness the fastest growth, growing at a CAGR of 21.0% throughout the forecast period. The growth of this segment is attributed to the integration and deployment of telecom cloud services. These services ensure effective functioning and improved operational efficiencies throughout the process. The services segment is further categorized into professional and managed services.
The professional services sub-segment dominated with a revenue share of 59.6% in 2021 and witnessing a CAGR of 20.2% during the forecast period. Professional services such as business analysis and consulting, design and architecture, integration, and deployment help to evaluate business cases and build solutions to minimize costs and deliver operational efficiency, security, and QoS.
The managed services sub-segment is anticipated to witness the fastest growth, growing at a CAGR of 22.0% throughout the forecast period. Managed services provide services that include network management, infrastructure management, data center management, backup and recovery, maintenance, and support. Managed services model allows an organization to outsource the operations, management, and delivery of processes to enable proactive network management, a lower total cost of ownership (TCO), and smart bundling.
Deployment Type Insights
In terms of deployment type, it is classified into private, public, and hybrid. Among these, private deployment held the largest revenue share of 56.4% in 2021. Private infrastructure is operated entirely by an organization hosted in the data center of the same organization, either on-premise or off-premise managed by a third party.
A private infrastructure enables telcos with improved control, better security & data privacy, specialized computational resources such as RAN, VNF, and edge apps and services, and cost-efficiency in underutilized capacities in an already existing data center. Moreover, the unused capacities can be utilized through cloud interfaces allowing organizations to utilize the same tools and benefit via cloud management software such as automated management, self-service interface, and the ability to sell unused capacities to partner companies.
Its ability to provide virtualized services has reduced complexity and maximized hardware usage at an affordable cost, and it offers overall control over the infrastructure and computational resources.
The hybrid segment is anticipated to witness the fastest growth, growing at a CAGR of 22.8% throughout the forecast period. A hybrid cloud is a composition of two or more clouds that are unique entities, at least one public cloud, and one private cloud. Hybrid infrastructure bounds these entities by proprietary or standardized technology, enabling data portability.
The growth of this segment is attributed to cost-effectiveness and scalability benefits, along with better security and data privacy. It allows telcos to optimize the operations with various patterns to manage workload. It improves resource allocation, optimizes infrastructure spending, provides enhanced organizational agility, and offers the ability to scale using the public infrastructure and controls available in the private cloud deployment.
Service Model Insights
The service model segment is classified into Platform as a Services (PaaS), Software as a Service (SaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). Among these, the Software as a Service (SaaS) segment is expected to dominate in 2021 with a revenue share of 55.7%. The IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) segment is estimated to grow at the fastest CAGR of 21.6% throughout the forecast period.
SaaS is a service that provides a business consequence, is purchased as a subscription, and is built on cloud-native Software. It includes a fully digitalized business experience and a fully automated service lifecycle for any carrier-grade network. Telecommunications firms may easily create agile application frameworks that optimize resource allocation and reduce overall complexity by utilizing SaaS technology. This improves corporate agility and enables telecommunications firms to accept a continual rate of change.
Before, telecommunications startups were pushed to the margins since dominant firms held a monopoly. However, the rise of SaaS technology has given small firms the ability to compete in the industry and gain their share of clients. SaaS enables them to provide enterprise-class services while reducing infrastructure overheads and prices.
IaaS is a low-cost, easy-to-access computing resource that gives enterprises more flexibility in trialing and testing business services and concepts. It enables businesses to avoid the typical risks associated with innovation, resulting in increased growth. The main advantage of IaaS is its potential to cut infrastructure expenses, shifting the cost base from CAPEX to OPEX.
The IaaS service model is appealing as it enables the migration of infrastructure to an IaaS solution with real-time business insights, reduced maintenance on on-premise data centers, and flexibility to scale IT resources as a separate service component. Still, the growth in data center expenditures across Asia-Pacific will drive availability and demand for IaaS in the future. This will result in enterprises shifting away from opportunistic and unstructured IaaS usage and toward more strategic projects.
Enterprise Size Insights
In terms of enterprise size, the industry is classified into large enterprises and SMEs. Among these, the large enterprise segment dominate in 2021 with a revenue share of 61.2%. The SMEs segment is expected to grow at a rapid CAGR of 21.0% throughout the forecast period. The large enterprises are partnerships and mergers to dominate the industry.
The adoption of cloud services at a substantial rate in large enterprises is propelling market growth. Large enterprises are making considerable investments in telecom cloud to address issues such as data security, privacy, and cloud connectivity failure. For example, in July 2022, AST SpaceMobile, Inc. and Nokia signed a five-year 5G deal. Under this deal, the companies will work together to expand universal coverage and connect underserved communities worldwide.
In May 2022, Nokia also announced the launch of the cloud-native IMS Voice Core product, which will help CSPs (Communication Service Providers) increase operational agility, simplify their network operations and decrease the cost of managing their network.
SMEs are increasingly growing cloud technology by adopting smart tech solution-cloud-based unified communications, which help small enterprises streamline their business operations. Additionally, the SMEs benefit significantly from the opportunities telecom cloud services offers, such as subscription-centered, cloud-based management systems consisting of end-to-end Wi-Fi solutions, automatic system upgrades, access points, and a cloud-native management/control plane.
Small and medium organizations/enterprises widely adopt it to gather analytical data about customer preferences and interactions for real-time decision-making. Adopting cloud-based communications at affordable costs will speed up the implementation process giving SMEs an edge to achieve global competitiveness.
Application Insights
The network, data storage, & computing segment dominated with a revenue share of 34.4% in 2021 and witnessing a CAGR of around 16.0% during the forecast period. It allows organizations to perform functions such as web application development, testing and developing new technologies, improving scalability, batch processing and storage, hosting, and handling peak workloads.
It also allows organizations to detect QoS degradation and implement techniques to manage traffic across the networks. These techniques involve optimizing the radio access network scheduler, limiting traffic, video optimization, and prioritization of mission-critical applications and different service plans.
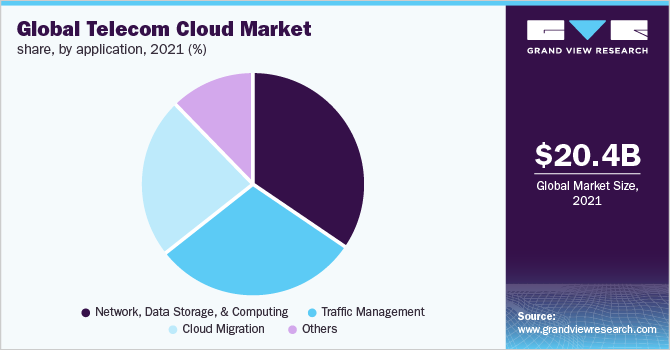
The cloud migration segment is anticipated to witness the fastest growth, growing at a CAGR of 22.9% throughout the industry forecast period. Cloud migration allows switching from one telecom cloud computing provider to another, enabling host data and applications with high security, better performance, and flexible prices.
Cloud migration provides a flexible pay-per-use model, self-service provisioning, greater elasticity, and redundancy, and includes different service models such as IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS. Cloud migration benefits include cloud security, managed operations, improved enterprise productivity, flexibility, and scalability, improved QoS, agile deployment of applications, and the Opex model.
Regional Insights
Global telecom cloud industry analysis is conducted across regions such as North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, South America, and Middle East & Africa. Among these, North America is expected to dominate in 2021, gaining a revenue share of 34.5%.
There is the increased use of hybrid telco cloud installations in the U.S. and Canada, which helps to embed best-in-class data analytics and artificial intelligence available in the public cloud sector to predict and fulfill consumers’ needs and preferences. The companies also use the cloud to eliminate silos databases, consolidate their customer data, provide an engaging Omni channel customer experience and create a 360-degree perspective of the consumer.
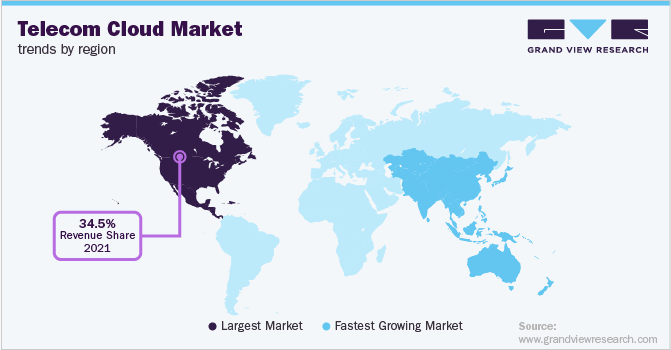
The rapid infrastructure growth in the Asia Pacific, particularly in South Korea, Japan, Singapore, Australia, India, and China, as well as the rapid development of the 5G network, presents high prospects for the telecom cloud to be implemented. Government supportive initiatives and policies motivate the companies to expand their business in this region, contributing to the economic growth.
The decrease in administrative and operational expenses, high demand for over-the-top cloud services, and awareness of telecom cloud among businesses are a few reasons for the growth of the regional industry.
Key Companies & Market Share Insights
The market is fragmented and is expected to witness an increase in competition owing to the presence of several players. The players are spending heavily on research and development activities to integrate cutting-edge technologies in telecom cloud marketing has intensified the competition among these players. Some prominent industry players include Ericsson, Nokia, Cisco, VMWare, Huawei, Fortinet, Mavenir, Metaswitch Networks, Affirmed Networks, and Juniper, among others.
These players are increasing their connectivity with the help of technology advancement to gain a competitive edge over their peers and capture a significant industry share. For example, in July 2022, AST SpaceMobile, Inc. and Nokia signed a five-year 5G deal. Under this deal, the companies will work together to expand universal coverage and connect underserved communities around the world. Some prominent players in the global telecom cloud market include:
-
Juniper Networks, Inc.
-
IBM Corporation
-
Mavenir
-
Metaswitch Network
-
Affirmed Networks
-
Fortinet
-
Orange
-
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
-
VMWare
-
Cisco
-
Nokia
-
Ericsson
Telecom Cloud Market Report Scope
|
Report Attribute |
Details |
|
Market size value in 2022 |
USD 24.21 billion |
|
Revenue forecast in 2030 |
USD 103.6 billion |
|
Growth Rate |
CAGR of 19.9% from 2022 to 2030 |
|
Base year for estimation |
2021 |
|
Historical year |
2017 - 2020 |
|
Forecast period |
2022 - 2030 |
|
Quantitative units |
Revenue in USD billion and CAGR from 2022 to 2030 |
|
Report coverage |
Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
|
Segments covered |
Component, deployment type, service model, application, enterprise size, region |
|
Regional scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; South America; Middle East & Africa |
|
Country scope |
U.S.; Canada; U.K.; Germany; France; China; India; Japan; South Korea; Brazil; Mexico |
|
Key companies profiled |
Juniper Networks, Inc.; IBM Corporation; Mavenir; Metaswitch Network; Affirmed Networks; Fortinet; Orange; Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.; VMWare; Cisco; Nokia; Ericsson |
|
Customization scope |
Free report customization (equivalent up to 8 analysts working days) with purchase. Addition or alteration to country, regional & segment scope. |
|
Pricing and purchase options |
Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. Explore purchase options |
Global Telecom Cloud Market Segmentation
The report forecasts revenue growth at the global, regional, and country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2017 to 2030. For this study, Grand View Research has segmented the global telecom cloud market report based on component, deployment type, service model, application, enterprise size, and region:
-
Component Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2017 - 2030)
-
Solution
-
Services
-
Professional Services
-
Managed Services
-
-
-
Deployment Type Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2017 - 2030)
-
Private
-
Public
-
Hybrid
-
-
Service Model Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2017 - 2030)
-
Software as a Service (SaaS)
-
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
-
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
-
-
Application Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2017 - 2030)
-
Network, Data Storage, and Computing
-
Traffic Management
-
Cloud Migration
-
Others
-
-
Enterprise Size Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2017 - 2030)
-
Large Enterprises
-
SMEs
-
-
Regional Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2017 - 2030)
-
North America
-
U.S.
-
Canada
-
-
Europe
-
U.K.
-
Germany
-
France
-
-
Asia-Pacific
-
China
-
India
-
Japan
-
South Korea
-
-
South America
-
Brazil
-
Mexico
-
-
Middle East & Africa
-
Frequently Asked Questions About This Report
b. The global telecom cloud market size was estimated at USD 20.4 billion in 2021 and is expected to reach USD 24.21 billion in 2022.
b. The global telecom cloud market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 19.9% from 2022 to 2030 to reach 103.6 by 2030.
b. North America dominated the telecom cloud market in 2021, gaining a market share of 34.5%. Factors such as increased use of hybrid telco cloud installations in the U.S. and Canada, which helps to embed best-in-class data analytics drives the growth of this market in North America region.
b. Some of the key players operating in the telecom cloud market include Ericsson, Nokia, Cisco, VMWare, Huawei, Fortinet, Mavenir, Metaswitch Networks, Affirmed Networks, and Juniper, among others
b. Key factors that are driving the telecom cloud market growth include rapid digital transformation between industries increased significant data consumption, and increased internet & mobile device penetration.
We are committed towards customer satisfaction, and quality service.
"The quality of research they have done for us has been excellent."