Singapore Real Estate Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report By Property (Residential, Commercial, Industrial), By Type (Sales, Rental), And Segment Forecasts, 2025 - 2030
- Report ID: GVR-4-68040-486-8
- Number of Report Pages: 80
- Format: PDF, Horizon Databook
- Historical Range: 2018 - 2024
- Forecast Period: 2025 - 2030
- Industry: Consumer Goods
Singapore Real Estate Market Size & Trends
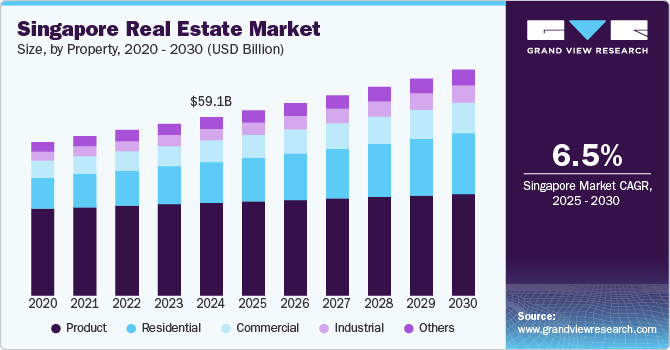
The Singapore real estate market size was valued at USD 59.08 billion in 2024 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 6.5% from 2025 to 2030. The growth of the real estate market in Singapore is driven by several key factors that reflect the evolving economic landscape and demographic trends. Affordable housing initiatives are a significant driver as the government continues to support projects aimed at providing accessible living options for residents. This focus on affordability is complemented by a growing demand for logistics and industrial real estate, fueled by Singapore's strategic position as a regional logistics hub and the rise of e-commerce, which necessitates more warehousing and distribution facilities.
Affordable housing projects in Singapore significantly impact the real estate market by enhancing accessibility and promoting homeownership among a broader segment of the population. The government’s commitment to providing affordable public housing through initiatives like the Housing Development Board (HDB) has resulted in one of the highest homeownership rates globally, exceeding 80% among citizens. These projects are essential for lower and middle-income families, as they enable home purchases through various subsidies and grants, making properties more financially attainable.
However, while these initiatives increase demand for HDB flats, they also contribute to rising prices in both the public and private housing markets. As homeowners sell their subsidized HDB flats, they often reinvest profits into private properties, thus driving up prices across the board. This cycle has led to concerns about affordability, particularly as the price-to-income ratio for HDB flats has shown an upward trend over the years, indicating that while subsidies help, they may also inadvertently fuel price inflation in the housing market.
Moreover, the government actively manages this dynamic through various policies aimed at maintaining market stability. Measures such as loan-to-value ratios and restrictions on speculative buying are designed to mitigate excessive price increases while ensuring that affordable housing remains a viable option for many Singaporeans. The ongoing development of new BTO flats and increased land sales for private housing are also strategies employed to balance supply and demand, ultimately aiming to stabilize property prices while promoting economic growth and social cohesion within the community.
Additionally, the office sector is undergoing transformation, with companies increasingly seeking locations outside traditional city centers to attract talent and create less dense work environments. This shift has been accelerated by the emergence of Singapore as a technology hub, where large tech firms are driving demand for both office spaces and co-working environments. The hospitality sector also plays a crucial role in market growth, bolstered by initiatives like the Singapore Tourism Board's BOOST program aimed at enhancing tourism and business travel, which are vital sources of revenue for hotel real estate.
Furthermore, Singapore's real estate market has demonstrated resilience despite global economic challenges. Private house prices have continued to rise for twelve consecutive quarters, indicating strong demand even amidst rising interest rates and inflation. The government's proactive land sales strategy has further stimulated investment activities, with significant transactions occurring in prime locations. Overall, the interplay of these factors-affordable housing, industrial demand, office space evolution, and robust tourism initiatives-positions Singapore's real estate market for sustained growth in the coming years.
The transformation of the office sector in Singapore is significantly driving the real estate market, influenced by evolving work patterns, demographic shifts, and strategic government policies. As companies increasingly adapt to hybrid work models, there is a notable shift in demand for office spaces that prioritize flexibility and employee well-being. Organizations are seeking locations outside traditional central business districts to create less dense environments that appeal to talent, reflecting a broader trend towards decentralization in commercial real estate. This has led to a growing interest in co-working spaces and flexible office arrangements, particularly among tech firms that are establishing Singapore as a regional technology hub.
Moreover, the limited supply of high-quality freehold office properties enhances their attractiveness. Recent developments, such as the successful launch of freehold strata offices like Solitaire on Cecil, indicate strong investor interest from ultra-high-net-worth individuals and family offices. These buyers are drawn to the potential for long-term capital appreciation amid regulatory changes that restrict the supply of new freehold strata offices. Such dynamics have resulted in substantial increases in transaction values for these properties, highlighting the resilience and appeal of the office sector even in a challenging economic environment.
Additionally, policy changes have redirected investor interest toward commercial properties. For instance, increased stamp duties on foreign residential purchases have made office investments more appealing as alternatives. This strategic pivot not only supports the growth of the office sector but also contributes to overall market stability by diversifying investment portfolios. As Singapore continues to enhance its status as a global business hub, the ongoing transformation of its office sector will remain a crucial driver of real estate market growth, fostering innovation and attracting both local and foreign investments.
The market faces several significant challenges that impact its growth and stability. Weak market demand is a critical challenge, highlighted by a notable decline in new home sales. Recent data indicates that new home sales dropped significantly, reflecting a cautious sentiment among buyers amid high interest rates and stringent government cooling measures. These regulations, while intended to maintain market stability, have suppressed demand and contributed to a decrease in transaction volumes, with some forecasts predicting the lowest sales levels in over a decade.
Additionally, foreign investment challenges have emerged due to global economic uncertainties and travel restrictions stemming from the COVID-19 pandemic. The reduction in foreign investments has particularly affected high-end property segments, where international buyers typically play a significant role. As foreign investment declines, market liquidity may also be impacted, raising concerns about overall market stability.
Property Insights
The residential segment accounted for the largest market share in 2024. Affordable housing initiatives remain a basis of the market, with the government actively promoting public housing through the Housing Development Board (HDB). This has resulted in a high homeownership rate, which is essential for maintaining social stability and economic growth. The government's commitment to providing affordable housing options ensures that a significant portion of the population can access homeownership, thus stimulating demand in the residential sector.
Additionally, demographic changes, including population growth and urbanization, contribute significantly to residential property demand. As Singapore continues to attract foreign talent and expatriates, the need for diverse housing options-ranging from affordable units to luxury condominiums-becomes increasingly pronounced. This demand is further fueled by an expanding middle class that seeks quality living spaces equipped with modern amenities.
Moreover, economic resilience plays a critical role in driving property growth. Despite global economic uncertainties, Singapore's economy has shown robust performance, which supports consumer confidence and investment in real estate. The anticipated growth of the residential market is also bolstered by a projected increase in wealthy individuals in the region, who view real estate as a stable investment opportunity.
The government's proactive land sales strategy has also facilitated new developments, ensuring a steady supply of residential properties to meet market demand. This approach helps mitigate price volatility and encourages developers to invest in new projects. Furthermore, recent initiatives aimed at enhancing urban living-such as the integration of green spaces and improved public transportation-make residential areas more attractive to potential buyers.
The commercial segment is expected to grow at a CAGR of 6.0% from 2024 to 2030. Government policies play a pivotal role, with initiatives aimed at enhancing the attractiveness of Singapore as a global business hub. The proactive approach to land sales and urban planning has facilitated the development of modern office spaces, particularly in emerging business districts outside the traditional central business area. This shift is in response to companies seeking less dense work environments that can attract talent while fostering employee well-being.
The rise of Singapore as a technology and financial services hub further propels demand for commercial properties, particularly office and co-working spaces. Large technology firms are expanding their footprints, driving up demand for flexible office solutions that accommodate hybrid work models. Additionally, the influx of family offices and investment firms seeking stable regulatory environments has created significant demand for boutique office spaces, contributing to a diversified tenant base.
Investor sentiment has also shown resilience, as evidenced by substantial commercial transactions in recent quarters. The commercial real estate sector recorded a remarkable increase in investment volume, with notable transactions highlighting strong interest from both local and foreign investors. Despite challenges such as high borrowing costs and fluctuating interest rates, the market has demonstrated robust activity, indicating pent-up demand for quality assets.
Moreover, the hospitality sector's recovery post-pandemic is enhancing the overall commercial real estate landscape. Initiatives like the Singapore Tourism Board's BOOST program aim to attract more tourists and business travelers, further stimulating demand for hotels and related commercial properties. This resurgence in tourism not only supports hospitality investments but also positively impacts retail spaces that cater to both locals and visitors.
Type Insights
The rental segment dominated the market in 2024. Renting offers significant advantages that appeal to a different demographic. The flexibility of renting is a major draw, especially for expatriates and young professionals who may not have long-term commitments in Singapore. Renting typically involves lower upfront costs compared to buying; tenants face minimal initial expenses, such as security deposits and the first month’s rent, without the burden of hefty down payments or ongoing maintenance responsibilities associated with property ownership. This flexibility allows renters to adapt quickly to changing circumstances, such as job relocations or shifts in personal plans.
Moreover, the current market conditions also influence these choices. With rising property prices and interest rates, many potential buyers are cautious about committing to a mortgage, leading them to opt for renting as a more financially prudent short-term solution. Additionally, the increasing availability of rental properties due to a growing supply in the market provides more options for those choosing to rent.
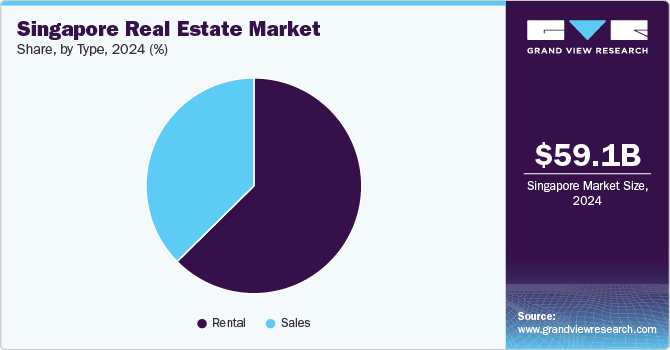
Home purchases in Singapore are expected to grow at a CAGR of 5.9% from 2024 to 2030. House purchases are primarily driven by the desire for stability and long-term investment. Owning a home allows individuals to build equity over time, benefiting from potential capital appreciation in Singapore’s historically strong property market. This sense of ownership provides security, particularly for families looking to establish roots in the community. Additionally, government policies that promote affordable housing options through the Housing Development Board (HDB) encourage homeownership among citizens, further stimulating demand for residential properties.
Key Singapore Real Estate Company Insights
The Singapore real estate company landscape is characterized by a mix of prominent domestic players and an influx of foreign investors, creating a moderately competitive environment. Key players in the market include UOL Group Limited, CapitaLand, City Developments Limited, GuocoLand Limited, and the Far East Organization. These companies dominate the residential and commercial sectors, leveraging their extensive experience and resources to capitalize on emerging opportunities in a rapidly evolving market.
Key Singapore Real Estate Companies:
- UOL Group Limited
- CapitaLand
- City Developments Limited
- GuocoLand Limited
- Far East Organization
- Genting Singapore
- Global Logistics Properties
- Ascendas Real Estate Investment Trust
- EL Development Pte Limited
- Frasers Property
Singapore Real Estate Market Report Scope
|
Report Attribute |
Details |
|
Market size value in 2025 |
USD 62.89 billion |
|
Revenue forecast in 2030 |
USD 85.96 billion |
|
Growth Rate (Revenue) |
CAGR of 6.5% from 2025 to 2030 |
|
Actuals |
2018 - 2024 |
|
Forecast period |
2025 - 2030 |
|
Quantitative units |
Revenue in USD million/billion, and CAGR from 2025 to 2030 |
|
Report coverage |
Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
|
Segments covered |
Property, type |
|
Country scope |
Singapore |
|
Key companies profiled |
UOL Group Limited; CapitaLand; City Developments Limited; GuocoLand Limited; Far East Organization; Genting Singapore; Global Logistics Properties; Ascendas Real Estate Investment Trust; EL; Development Pte Limited; Frasers Property |
|
Customization scope |
Free report customization (equivalent up to 8 analysts working days) with purchase. Addition or alteration to country, regional & segment scope. |
|
Pricing and purchase options |
Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. Explore purchase options |
Singapore Real Estate Market Report Segmentation
This report forecasts revenue growth at the country level and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends and opportunities in each of the sub-segments from 2018 to 2030. For this study, Grand View Research has segmented the Singapore real estate market report on the basis of property, and type:
-
Property Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2018 - 2030)
-
Residential
-
Commercial
-
Industrial
-
Others
-
-
Type Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2018 - 2030)
-
Sales
-
Rental
-
Frequently Asked Questions About This Report
b. The Singapore real estate market was estimated at USD 59.08 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 62.89 billion in 2025.
b. The Singapore real estate market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 6.5% from 2025 to 2030, reaching USD 85.96 billion by 2030.
b. Residential real estate products accounted for a market share of 47.12% in 2024. Affordable housing initiatives remain a basis of the market, with the government actively promoting public housing through the Housing Development Board (HDB). This has resulted in a high homeownership rate, which is essential for maintaining social stability and economic growth.
b. Some of the key players operating in the Singapore real estate market are UOL Group Limited; CapitaLand; City Developments Limited; GuocoLand Limited; Far East Organization; Genting Singapore; Global Logistics Properties; Ascendas Real Estate Investment Trust; EL Development Pte Limited; Frasers Property.
b. The growth of the real estate market in Singapore is driven by several key factors that reflect the evolving economic landscape and demographic trends.
We are committed towards customer satisfaction, and quality service.
"The quality of research they have done for us has been excellent."