Gas Pipeline Infrastructure Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report By Operation (Gathering, Transmission, Distribution), By Application (Compressor Station, Metering Station), By Region, And Segment Forecasts, 2025 - 2030
- Report ID: GVR-4-68038-237-2
- Number of Report Pages: 110
- Format: PDF
- Historical Range: 2018 - 2024
- Forecast Period: 2025 - 2030
- Industry: Energy & Power
Gas Pipeline Infrastructure Market Trends
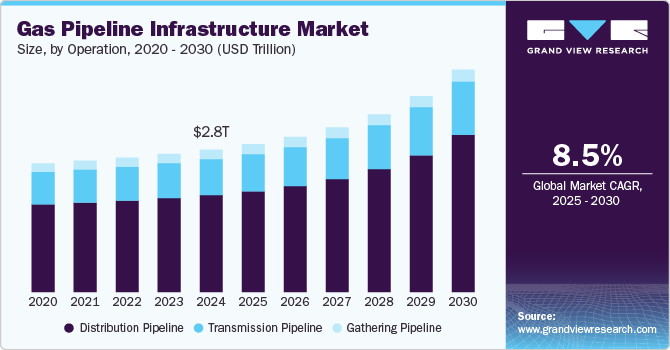
The global gas pipeline infrastructure market size was estimated at USD 2,800.53 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 8.5% from 2025 to 2030. The primary driver of gas pipeline infrastructure development is the growing global demand for natural gas as a cleaner fossil fuel alternative. As countries work to reduce their carbon emissions while maintaining energy security, natural gas serves as a crucial bridge fuel in the energy transition.
The rising global demand for energy is a key driving factor of the gas pipeline infrastructure market. With growing populations and rapid urbanization, particularly in developing economies such as India, China, and Brazil, natural gas is becoming a preferred energy source due to its lower carbon emissions compared to coal and oil. For example, China's National Energy Administration is heavily investing in expanding its gas pipeline network to reduce coal dependency and meet energy demands. Additionally, the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) projects a significant increase in global natural gas consumption, fueling the need for expanded and modernized pipeline networks.
Governments and industries worldwide are transitioning to cleaner energy to meet climate goals and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Natural gas, being a cleaner-burning fossil fuel, is gaining prominence in energy generation and industrial processes. This trend has led to initiatives such as the European Union’s “Green Deal,” which aims to enhance gas infrastructure to support the transition to hydrogen and other renewable gases in the future. Such policies drive investment in new pipelines and the retrofitting of existing ones, ensuring a steady market growth trajectory.
The growth in liquefied natural gas (LNG) production and export facilities is a critical factor bolstering gas pipeline infrastructure development. LNG requires an extensive network of pipelines for transportation from production sites to liquefaction plants and distribution hubs. As major LNG exporters, the U.S. and Qatar are investing heavily in pipeline projects to enhance connectivity and export capacity. For instance, the U.S.’s Sabine Pass Liquefaction project has spurred significant pipeline development to transport gas from shale fields to export terminals.
Operation Insights
The distribution pipeline segment registered the largest revenue market share of over 68.1% in 2024 and is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR of 3.6% during the forecast period. The distribution pipeline segment is primarily driven by urbanization and the increasing adoption of natural gas for domestic heating, cooking, and small-scale industrial applications. The push for energy efficiency and cleaner fuels in residential and commercial sectors is boosting the growth of the segment.
Transmission pipelines are large-diameter, high-pressure pipelines that transport processed natural gas from processing facilities to storage facilities or large distribution hubs across long distances. These pipelines serve as the backbone of the gas supply chain, enabling interstate and international gas transportation. Rising cross-border trade of natural gas, supported by liquefied natural gas (LNG) terminals, further fuels the need for robust transmission networks.
Gathering pipelines collect raw natural gas from production sites, such as wells, offshore rigs, and transport it to processing facilities. They form the initial stage of the gas pipeline network, consolidating gas from multiple sources for further processing and refinement. The gathering pipeline segment growth is driven by increased exploration and production activities in shale gas and unconventional reserves.
Application Insights
The metering station segment accounted for the largest revenue market share of over 75.0% in 2024 and is expected to grow at a faster CAGR of 8.7% during the forecast period. The increasing emphasis on accurate gas measurement for financial and regulatory purposes drives the growth of metering stations. Furthermore, the rise in domestic and industrial gas consumption, along with the integration of advanced metering technologies such as smart meters, bolsters the need for metering stations.
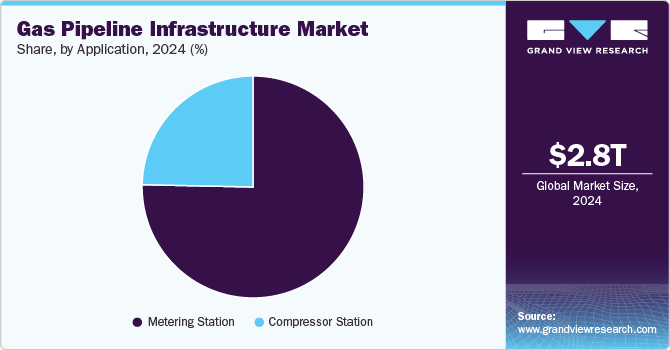
A compressor station is a critical component of gas pipeline infrastructure, designed to maintain the pressure and flow of natural gas as it travels through long-distance pipelines. These stations are located at strategic intervals along the pipeline to ensure the efficient and uninterrupted delivery of natural gas to end users, including industrial facilities, power plants, and residential areas. The expansion of cross-border and inter-regional gas pipeline projects boosts the demand for compressor stations to support high-pressure and long-distance gas transport.
Regional Insights
North America dominated the market and accounted for the largest revenue share of over 54.0% in 2024. The region's shale gas revolution has been a primary driver, particularly in the U.S., where areas such as the Permian Basin, Marcellus Shale, and Eagle Ford have transformed the natural gas landscape. This abundance of natural gas resources has necessitated extensive pipeline development to transport gas from production sites to consumption centers. For example, projects such as the mountain valley pipeline (MVP) and the Permian highway pipeline have been crucial in connecting gas-rich regions to markets, with the MVP alone designed to transport approximately 2.0 billion cubic feet of natural gas per day from northwestern West Virginia to southern Virginia.

U.S. Gas Pipeline Infrastructure Market Trends
The U.S. government's push for energy independence and its transition toward cleaner energy sources has driven the growth of gas pipeline infrastructure market. Natural gas is viewed as a bridge fuel in the transition from coal to renewable energy, leading to increased investment in gas transportation infrastructure. This is evidenced by the development of pipeline networks connecting to LNG export terminals along the Gulf Coast, such as the Calcasieu Pass and Sabine Pass facilities, which have transformed the U.S. into a major LNG exporter. Additionally, the replacement and modernization of aging pipeline infrastructure, some of which dates to the 1950s and 1960s, has created a substantial market for pipeline construction and maintenance services.
Europe Gas Pipeline Infrastructure Market Trends
European environmental policies and the role of natural gas as a transition fuel have also significantly influenced gas infrastructure development in the region. As part of the European Green Deal, many countries are upgrading their existing pipeline infrastructure to make it hydrogen-ready, anticipating the future transition to clean energy sources. For instance, the European Hydrogen Backbone initiative aims to repurpose existing gas infrastructure for hydrogen transport, with companies such as Gasunie and Enagás S.A. leading major retrofit projects. The Netherlands has been pioneering in adapting its gas infrastructure for future hydrogen use.
Asia Pacific Gas Pipeline Infrastructure Market Trends
The region's rapid industrialization, particularly in countries such as China, India, and Southeast Asian nations, has created an unprecedented demand for natural gas as a cleaner alternative to coal for power generation and industrial processes. This has necessitated massive investments in pipeline infrastructure to ensure reliable gas transportation from production sites to consumption centers. Major infrastructure projects exemplify this trend, such as China's West-to-East Gas Pipeline network, which spans over 8,800 kilometers and connects the gas-rich Xinjiang region to energy-hungry eastern provinces. Similarly, India's national gas grid expansion plan aims to add over 15,000 kilometers of pipeline infrastructure to increase gas accessibility across the country.
Key Gas Pipeline Infrastructure Company Insights
The competitive environment of the global gas pipeline infrastructure market is characterized by the presence of a mix of well-established players and emerging companies, all vying for market share in a rapidly evolving sector. Key players such as Enbridge Inc., Kinder Morgan, and Gazprom dominate the market with extensive networks, robust technological capabilities, and strategic partnerships. Emerging players are leveraging innovations in leak detection systems, automation, and material advancements to carve out niches. Regional markets are shaped by government investments, energy demand patterns, and geopolitical influences, further intensifying competition. Additionally, the rising demand for natural gas as a cleaner energy source has spurred aggressive expansion strategies, including mergers, acquisitions, and joint ventures.
Key Gas Pipeline Infrastructure Companies:
The following are the leading companies in the gas pipeline infrastructure market. These companies collectively hold the largest market share and dictate industry trends.
- Enbridge Inc.
- Gazprom
- TransCanada Pipelines Limited
- Kinder Morgan
- Pembina Gas Infrastructure
- Saipem
- Enagás S.A.
- Bechtel Corporation
- Assam Gas Company Ltd.
- McDermott
Recent Developments
-
In September 2024, Apollo Global Management entered into an agreement with BP for Apollo-managed funds to acquire a non-controlling stake in BP Pipelines TAP Limited, which holds a 20.0% share in the Trans Adriatic Pipeline (TAP). This transaction is valued at approximately USD 1.0 billion. The Trans Adriatic Pipeline is crucial for transporting natural gas from Azerbaijan to Europe, specifically Greece and Italy, as part of the Southern Gas Corridor.
-
In July 2024, Engie, the French energy company, has announced a partnership with Macquarie Asset Management from Australia to expand the Mayakan natural gas pipeline in Mexico. Macquarie will acquire a 50% stake in the project for USD 360.0 million. The total enterprise value of the pipeline upon completion is projected to be up to USD 3.0 billion. The new pipeline will span 700 kilometers across the Yucatán Peninsula, effectively doubling the natural gas transportation capacity for the region. It will traverse the states of Chiapas, Tabasco, Campeche, and Yucatán.
-
In May 2024, Nesma & Partners formed a joint venture with Italian firm SICIM to work on two Master Gas projects for Saudi Aramco, focusing on nearly 500 km of pipeline construction in Saudi Arabia. This collaboration is pivotal for enhancing the energy sector and aligns with Saudi Vision 2030 objectives for economic diversification and industrial growth.
Gas Pipeline Infrastructure Market Report Scope
|
Report Attribute |
Details |
|
Market size value in 2025 |
USD 2,907.91 billion |
|
Revenue forecast in 2030 |
USD 4,372.16 billion |
|
Growth rate |
CAGR of 8.5% from 2025 to 2030 |
|
Historical data |
2018 - 2024 |
|
Forecast period |
2025 - 2030 |
|
Quantitative units |
Volume in Thousand Kilometers, Revenue in USD Billion, and CAGR from 2025 to 2030 |
|
Report coverage |
Revenue forecast, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |
|
Segments covered |
Operation, application, region |
|
Regional scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Central & South America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Country Scope |
U.S.; Canada; Mexico; Germany; UK; Russia; China; India; Australia; Brazil; Argentina; Saudi Arabia; Qatar |
|
Key companies profiled |
Enbridge Inc.; Gazprom; TransCanada Pipelines Limited; Kinder Morgan; Pembina Gas Infrastructure; Saipem; Enagás S.A.; Bechtel Corporation; Assam Gas Company Ltd.; McDermott |
|
Customization scope |
Free report customization (equivalent up to 8 analyst’s working days) with purchase. Addition or alteration to country, regional & segment scope |
|
Pricing and purchase options |
Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. Explore purchase options |
Global Gas Pipeline Infrastructure Market Report Segmentation
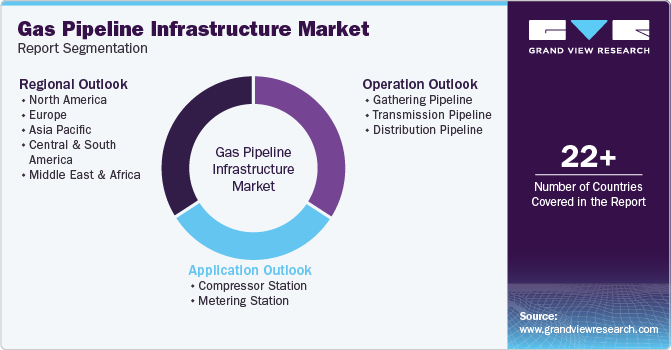
This report forecasts revenue growth at global, regional, and country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2018 to 2030. For this study, Grand View Research has segmented the gas pipeline infrastructure market report on the basis of operation, application, and region:
-
Operation Outlook (Volume, Thousand Kilometers; Revenue, USD Billion, 2018 - 2030)
-
Gathering Pipeline
-
Transmission Pipeline
-
Distribution Pipeline
-
-
Application Outlook (Volume, Thousand Kilometers; Revenue, USD Billion, 2018 - 2030)
-
Compressor Station
-
Metering Station
-
-
Regional Outlook (Volume, Thousand Kilometers; Revenue, USD Billion, 2018 - 2030)
-
North America
-
U.S.
-
Canada
-
Mexico
-
-
Europe
-
Germany
-
UK
-
Russia
-
-
Asia Pacific
-
China
-
India
-
Australia
-
-
Central & South America
-
Brazil
-
Argentina
-
-
Middle East & Africa
-
Saudi Arabia
-
Qatar
-
-
Frequently Asked Questions About This Report
b. The global gas pipeline infrastructure market size was estimated at USD 2,800.53 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 2,907.91 billion in 2025.
b. The global gas pipeline infrastructure market is expected to witness a compound annual growth rate of 8.5% from 2025 to 2030 to reach USD 4,372.16 billion by 2030.
b. Distribution pipeline segment captured a market share of nearly 68.10% in 2024 owing to rising natural gas consumption in end-use segments such as gas fired power plants and chemical sector.
b. Some key players operating in the gas pipeline infrastructure market Enbridge, Gazprom, TransCanada, Kinder Morgan, Saipem, Alliance Pipelines.
b. Key factors that are driving the market growth include rising government investments to enhance gas accessibility along with need to upgrade the existing pipeline network across several regions.
We are committed towards customer satisfaction, and quality service.
"The quality of research they have done for us has been excellent."