Connected Ship Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report By Ship (Commercial, Defense), By Installation (Onboard, Onshore), By Application (Vessel Traffic Management, Fleet Operations), By Region, And Segment Forecasts, 2025 - 2030
- Report ID: GVR-4-68038-206-8
- Number of Report Pages: 100
- Format: PDF, Horizon Databook
- Historical Range: 2018 - 2023
- Forecast Period: 2025 - 2030
- Industry: Technology
Connected Ship Market Size & Trends
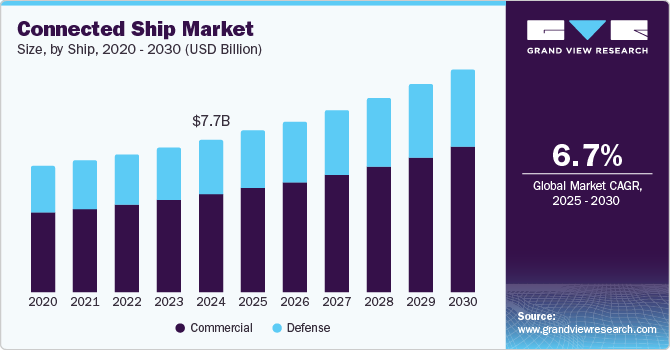
The global connected ship market size was valued at USD 7.69 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.7% from 2025 to 2030. Operators in the maritime sector are looking to continuously improve their functioning and enable data-driven decision-making, which has led to the rapid adoption of connected ship technology. The significance of connected ships lies in their ability to integrate advanced digital technologies that can help boost operational efficiency, safety, environmental sustainability, and cost-effectiveness. They are equipped with Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, communication systems, and data analytics systems that allow for the real-time monitoring and remote control of vessels.
The shipping industry has increasingly embraced digital technologies to streamline operations in recent years. The extensive use of solutions that capture data related to vessel performance, navigation, fuel consumption, cargo management, and crew well-being has become a leading factor for market expansion. Furthermore, the rising frequency of traffic congestions at major canals and the need for efficient port traffic management are anticipated to fuel the growth of the connected ship industry in the coming years. For instance, connected ships can communicate their estimated time of arrival (ETA) and other relevant information, such as cargo details or special requirements, directly to port authorities and terminal operators. This helps authorities anticipate arrivals and better allocate resources such as docking spaces and tugboats, substantially reducing delays and wait times. Moreover, the provision of updates enables them to dynamically adjust berth assignments. Ships can be directed to the most suitable berth based on cargo, vessel size, and expected departure times, thus minimizing waiting times and optimizing the use of available docking spaces.
The connected ship industry is rapidly evolving, with various projects and initiatives aiming to enhance maritime operations' safety, efficiency, sustainability, and automation. These projects span from pilot programs and research initiatives to large-scale deployments by shipping companies, port operators, and technology providers. For instance, the Connected Ship project funded by Nordic Innovation aims to showcase a digitalization platform deployed on a ship. This platform leverages solutions and technologies from various smart city projects in combination with control systems from the maritime industry, as well as communication protocols and environmental prerequisites. The project is expected to prepare ships for future interactions with trucks, harbors, passengers, cargo, and other smart micro-systems. The platform horizontally collects and controls non-critical data, handles data access policies, and enables AI, data analytics, and automation to connect and receive access to data and devices. Such functions are expected to support energy efficiency, predictive maintenance, and cybersecurity objectives.
Ship Insights
The commercial segment accounted for the largest revenue share of 64.0% in the connected ship market in 2024, aided by the increasing presence of commercial fleets worldwide. Increasing trade activities between major economies have created a significant demand for using connected technologies that can reduce travel times by selecting the shortest route to a destination depending on parameters such as traffic congestion and port availability. Customers increasingly expect real-time visibility into the status of their shipments. Connected ships, with their integrated tracking and monitoring capabilities, allow shipping companies to offer customers updates regarding cargo location, condition, and expected delivery times, thus enhancing service quality and customer satisfaction.
The defense segment is anticipated to grow at a steady CAGR during the forecast period in the connected ship industry. With naval bases across several countries looking to modernize their operations and strengthen their strategic positioning, connected technologies have emerged as a highly effective solution. Their extensive use is reshaping how naval forces operate, enhancing their capabilities across a range of areas such as situational awareness, autonomous operations, maintenance and logistics, command & control, and cybersecurity. Connected ships are facilitating the deployment of unmanned combat systems, which can perform reconnaissance, surveillance, anti-submarine warfare (ASW), and even strike missions without risking crew members' lives. These systems can be controlled remotely and share real-time information with other military assets. Such advantages are expected to aid segment expansion.
Installation Insights
The onboard segment accounted for a leading revenue share in the global market for connected ships in 2024. The presence of connected technologies such as IoT sensors, advanced communication systems, and AI-based analytics enables instantaneous data collection and decision-making, improving the vessel’s overall performance while reducing costs and environmental impacts. Advanced onboard systems can autonomously adjust the ship’s course based on real-time data, using AI-driven algorithms for collision avoidance, route optimization, and weather condition assessment. The availability of onboard systems further enables the continuous monitoring of machinery and systems for early signs of wear and tear, reducing the risk of breakdowns and improving overall operational uptime.
The onshore segment is anticipated to grow at a significant CAGR from 2025 to 2030 in the global market. Onshore technologies involve fleet management systems, port operations, command centers, and other land-based infrastructure that monitor, manage, and interact with ships during their voyages and at port. These technologies are crucial for coordinating and optimizing the overall logistics network that supports the vessel’s journey, enhancing operational efficiencies, and providing critical decision-making support to shore-based operators. Onshore connected systems can offer route planning tools and dynamic routing suggestions to optimize voyage times and reduce fuel consumption based on weather conditions, port traffic, and other relevant factors. Additionally, authorities and regulatory bodies can access real-time data from ships to ensure compliance with environmental standards. This includes verification of emissions data, fuel usage, and ballast water treatment status.
Application Insights
The vessel traffic management segment accounted for a leading revenue share in the global connected ship industry in 2024 and is further expected to grow at the fastest CAGR during the forecast period. Vessel traffic management (VTM) involves the management of vessel movements in port areas, shipping lanes, and coastal regions to ensure safe, efficient, and environmentally sustainable maritime traffic. With the integration of connected technologies, this function has become more data-driven and automated, resulting in improved safety, reduced congestion, optimized operations, and enhanced communication between vessels and port authorities. An Automatic Identification System (AIS) is one of the most widely used technologies for real-time vessel tracking. Ships are equipped with AIS transponders that broadcast their position, speed, heading, and other data to nearby vessels and shore-based authorities. Their continuous tracking allows vessel traffic managers to monitor vessels across a region, improving situational awareness and preventing collisions.
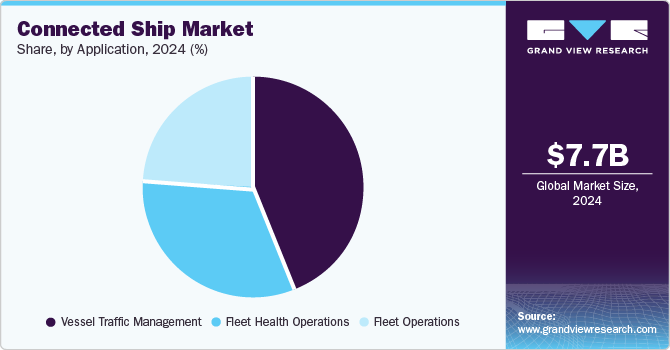
The fleet operations segment is anticipated to advance at a significant CAGR from 2025 to 2030. Fleet operations involve travel route decisions, trade information management, and asset protection and inspection tasks. A large number of systems can be simultaneously monitored to prevent any misalignments with planned schedules. The adoption of a centralized system enables convenience in control over every operation, which aids segment demand. Connective technologies can provide insights into a vessel’s fuel efficiency by monitoring fuel consumption in real-time. Operators can adjust routes, vessel speed, or operational procedures to minimize fuel usage, lowering operational costs and reducing the environmental footprint. Connected technologies further provide remote monitoring of onboard systems, allowing shore-based teams to assist the crew with troubleshooting and maintenance issues. Additionally, crew performance data can be gathered and analyzed for improved training and support.
Regional Insights
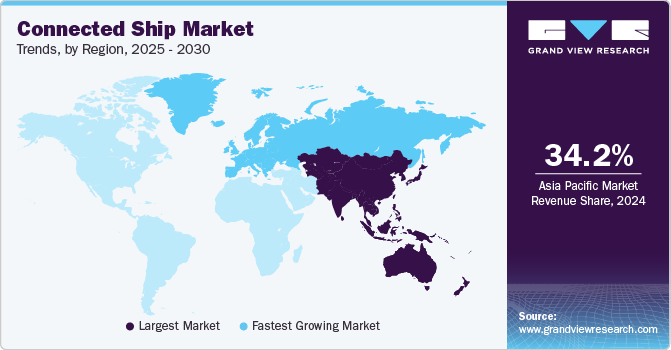
The Asia Pacific connected ship market accounted for a leading revenue share of 34.2% globally in 2024. Shipping companies in the region are increasingly looking to reduce operating costs, including fuel consumption, maintenance costs, and labor. Connected ships, with real-time data and analytics, can optimize fuel use, improve routing, and reduce delays. Moreover, governments and private organizations in the Asia Pacific have been investing substantially in upgrading port infrastructure to support digital transformation. Countries such as China, India, Japan, and Australia offer significant potential for the development of such ports. These smart ports create an ecosystem where connected ships can easily integrate with port systems for smoother operations, reducing bottlenecks and improving logistics efficiency.
China Connected Ship Market Trends
China accounted for the largest revenue share in the regional market in 2024. The government and private sectors in the economy are investing heavily in digital transformation. State-owned and private shipping companies are increasingly integrating connected technologies into their fleets. These investments are enabling the growth of smart shipping technologies and have transformed China into a leader in connected vessels in this region. Moreover, China’s maritime sector is heavily involved in global trade activities, with major shipping routes connecting China to the rest of the world. According to the ‘One Hundred Ports 2024’ report by Lloyd’s List, the country’s container volume share at the 100 biggest global seaports grew from 40.2% in 2022 to 41.3% in 2023. Thus, the significant movement of vessels across international waters has made connected ships a vital part of enhancing the visibility and reliability of global supply chains.
Europe Connected Ship Market Trends
Europe is expected to advance at the highest CAGR from 2025 to 2030 in the connected ships market. The increasing demand for connected ships in this region is driven by a combination of regulatory, technological, economic, and environmental factors that align with the region’s broader goals of sustainability, efficiency, and innovation in the maritime sector. Europe has some of the most stringent environmental regulations, including those set by the European Union (EU) and other bodies such as the International Maritime Organization (IMO). The EU’s Green Deal and the IMO’s push for carbon emission reductions are significant drivers aiding the adoption of connected technologies in ships and other vessels. Moreover, organizations such as the European Maritime Safety Agency (EMSA) and the Baltic and International Maritime Council (BIMCO) encourage industry-wide cooperation in adopting new technologies and creating common standards for connected vessels. These standards streamline the implementation of connected ship technologies, making it easier for operators to integrate them across fleets and regions.
Germany accounted for the largest revenue share in the European market for connected ships in 2024 and is further expected to maintain its position during the forecast period. Germany is home to major ports such as Hamburg, Bremerhaven, and Wilhelmshaven, which are investing significantly in transforming into “smart ports.” Smart ports involve the comprehensive use of automation, IoT, and AI technologies to streamline logistics, improve cargo handling, and increase port efficiency. In October 2024, the German government launched the National Action Plan for Climate-Friendly Shipping to boost investments and accelerate the German industry’s maritime energy transition. Such initiatives are expected to expand the deployment of connected solutions that can conduct real-time monitoring of fuel consumption, emissions, and compliance with environmental regulations in the maritime sector.
North America Connected Ship Market Trends
North America is anticipated to witness moderate growth in the connected ship market during the forecast period. Companies in regional economies such as the U.S. and Canada are increasingly adopting smart shipping technologies that integrate sensors, IoT devices, and data analytics platforms, helping fleets become more efficient and adaptable. Furthermore, the high traffic levels on major trade routes such as the East Coast and the Gulf of Mexico have prioritized safety in North America’s maritime industry, resulting in the increased deployment of connected systems on vessels. For instance, collision avoidance systems, real-time weather data, and remote diagnostics features allow operators to avoid accidents and minimize human error risks. These factors are expected to create positive growth avenues for market players operating in this region.
The U.S. accounted for a dominant revenue share in the regional market in 2024 on account of factors including regulatory requirements, sustainability initiatives, technological advancements, and industry requirements for operational efficiency. The U.S. Coast Guard enforces various safety regulations, including the Vessel Incidental Discharge Act (VIDA) and the Ballast Water Management Program. Connected ships can monitor water discharge, ballast water treatment systems, and other environmental parameters to ensure compliance with these regulations. Moreover, several major ports on both the East and West coasts, such as Los Angeles, Seattle, Houston, and New York/New Jersey, have aided market expansion, as these ports are transforming into smart ports. Connected ships are essential for the seamless integration of vessels with these smart port systems, enabling automated docking and port operations, optimized scheduling and logistics, and real-time cargo tracking.
Key Connected Ship Company Insights
Some of the major companies involved in the global connected ship industry include Sperry Marine, Wärtsilä, and Danelec Marine A/S, among others.
-
Sperry Marine, part of the Northrop Grumman Corporation, is a global supplier of navigation, communication, information, and automation systems for commercial marine and naval markets. The company is known for its connected ship solution, which serves both commercial and defense segments under VisionMaster Integrated Bridge System (IBS) and Defence Integrated Bridge System, respectively. The company has an extensive international presence, catering to clients in Asia, Europe, and the Americas.
-
Wärtsilä is a Finland-based company that specializes in manufacturing and servicing power sources and equipment for the marine and energy markets. Under the marine segment, the company offers solutions for different application areas, including passenger vessels (cruise ships and ferries), offshore vessels, special-purpose vessels, and merchant vessels (carriers, bulkers, and tankers). Wärtsilä launched its ‘Smart Marine Ecosystem’ initiative to drive digital transformation in the shipping industry. The project integrates a number of connected technologies, including IoT, data analytics, and AI, to enhance vessel performance, optimize operations, and improve fleet management.
Key Connected Ship Companies:
The following are the leading companies in the connected ship market. These companies collectively hold the largest market share and dictate industry trends.
- Schneider Electric
- Sperry Marine B.V.
- YALTES Electronic and Information Systems Production and Trade Inc.
- Wärtsilä
- Kongsberg Maritime
- Danelec Marine A/S
- Anglo-Eastern
- Rockwell Automation
- Marlink B.V.
- HD Hyundai Heavy Industries Co., Ltd.
Recent Developments
-
In December 2024, Marlink announced that it would provide Thoresen Shipping’s fleet with its Sealink NextGen solution, aiding Thoresen Shipping in its digitalization initiatives. As part of the agreement, 24 vessels would be integrated with VSAT and Starlink LEO services, aiding Thoresen Shipping in optimizing its operations and improving customer support via enhanced network security and application performance.
-
In May 2024, Danelec and DanPilot, a Denmark-based piloting organization, announced the development of an innovative remote piloting solution at the European Maritime Day conference. The new technology involves the integration of navigation and operational solutions, enabling operators to pilot the ship safely without requiring their onboard presence. This is expected to improve safety and optimize logistics while lowering environmental impact. Moreover, ships can maintain a planned speed that would reduce fuel costs and meet scheduled ETD (estimated time of departure) and ETA (estimated time of arrival).
Connected Ship Market Report Scope
|
Report Attribute |
Details |
|
Market size value in 2025 |
USD 8.13 billion |
|
Revenue forecast in 2030 |
USD 11.25 billion |
|
Growth rate |
CAGR of 6.7% from 2025 to 2030 |
|
Base year for estimation |
2024 |
|
Historical data |
2018 - 2023 |
|
Forecast period |
2025 - 2030 |
|
Quantitative units |
Revenue in USD million/billion, and CAGR from 2025 to 2030 |
|
Report coverage |
Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
|
Segments covered |
Ship, installation, application, region |
|
Regional scope |
North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, MEA |
|
Country scope |
U.S., Canada, Mexico, Germany, U.K., France, China, Japan, India, South Korea, Australia, Brazil, UAE, Saudi Arabia, South Africa |
|
Key companies profiled |
Schneider Electric; Sperry Marine B.V.; YALTES Electronic and Information Systems Production and Trade Inc.; Wärtsilä; Kongsberg Maritime; Danelec Marine A/S; Anglo-Eastern; Rockwell Automation; Marlink B.V.; HD Hyundai Heavy Industries Co., Ltd. |
|
Customization scope |
Free report customization (equivalent up to 8 analysts working days) with purchase. Addition or alteration to country, regional & segment scope. |
|
Pricing and purchase options |
Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. Explore purchase options |
Global Connected Ship Market Report Segmentation
This report forecasts revenue growth at the global, regional, and country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2018 to 2030. For this study, Grand View Research has segmented the global connected ship market report based on ship, installation, application, and region:
-
Ship Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
-
Commercial
-
Defense
-
-
Installation Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
-
Onboard
-
Onshore
-
-
Application Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
-
Vessel Traffic Management
-
Fleet Operations
-
Fleet Health Operations
-
-
Regional Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
-
North America
-
U.S.
-
Canada
-
Mexico
-
-
Europe
-
Germany
-
U.K.
-
France
-
-
Asia Pacific
-
China
-
India
-
Japan
-
South Korea
-
Australia
-
-
Latin America
-
Brazil
-
-
MEA
-
Saudi Arabia
-
UAE
-
South Africa
-
-
Frequently Asked Questions About This Report
b. The global connected ship market size was estimated at USD 6.1 billion in 2019 and is expected to reach USD 6.3 billion in 2020.
b. The global connected ship market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 5.4% from 2020 to 2027 to reach USD 9.2 billion by 2027.
b. Asia Pacific dominated the connected ship market with a share of 32.3% in 2019. This is attributable to the presence of some of the busiest international ports and trade routes in the region.
b. Some key players operating in the connected ship market include General Electric; Emerson; Warstila Corporation; Kongsberg; Sperry Marine; Yaltes; Danelec Electronics; and Schneider Electric.
b. Key factors that are driving the market growth include the increasing need to monitor the operations, functioning, and the voyage path of ships on a centralized platform.
We are committed towards customer satisfaction, and quality service.
"The quality of research they have done for us has been excellent."