- Home
- »
- Clinical Diagnostics
- »
-
China Lung Cancer Screening Market, Industry Report, 2030GVR Report cover
![China Lung Cancer Screening Market Size, Share & Trend Report]()
China Lung Cancer Screening Market Size, Share & Trend Analysis Report By Cancer (Non-small Cell, Small Cell), By Diagnosis (Low Dose Spiral CT Scan), By End Use (Hospitals and Clinics), By Region, And Segment Forecasts, 2024 - 2030
- Report ID: GVR-4-68040-456-5
- Number of Report Pages: 160
- Format: PDF, Horizon Databook
- Historical Range: 2018 - 2023
- Forecast Period: 2024 - 2030
- Industry: Healthcare
China Lung Cancer Screening Market Trends
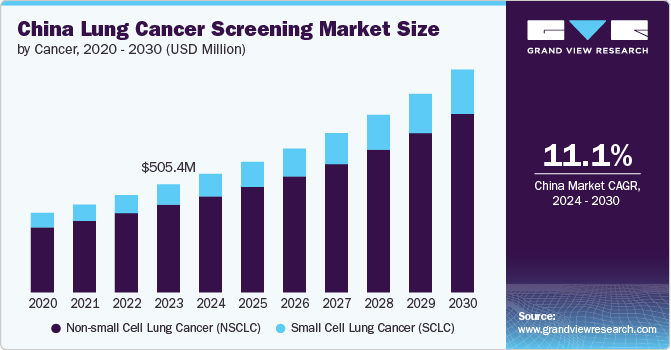
The China lung cancer screening market size was estimated at USD 505.17 million in 2023 and is projected to grow at CAGR of 11.09% from 2024 to 2030. The growth of the market is driven by several key factors, including the high prevalence of lung cancer, advances in screening technology, supportive government policies, and increasing awareness about early detection. According to the Shanghai Municipal People's Government, in June 2023, lung cancer was observed as one of the most common and deadliest tumors in China, with approximately 800,000 new cases reported annually and around 70.0% of patients diagnosed at advanced or terminal stages, highlighting the urgent need for effective screening solutions to improve early diagnosis and treatment outcomes.
According to the Journal of Thoracic Oncology, lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related deaths in China, accounting for nearly 19.2% of all deaths. This high prevalence drives a significant demand for effective screening and early detection solutions. According to the study published by National Library of Medicines in July 2023, the heavy burden in China is partly due to the large population. China has the largest number of smokers in the world and consumes about 40% of the world's tobacco every year. In addition, the widespread exposure to secondhand smoke affects about 70% of the population annually, contributing to approximately 60,000 lung cancer deaths each year. This severe public health burden in China drives the demand for advanced screening solutions to mitigate the impact of this prevalent disease.
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly impacted the market in China by accelerating the adoption and need for advanced diagnostic solutions. As the pandemic heightened awareness about respiratory health, it inadvertently increased the focus on early cancer detection, particularly for lung cancer. Lung cancer, which is one of the most common in China, saw a rise in screening demand due to the overlapping symptoms with COVID-19, such as persistent coughs and chest discomfort. According to the estimates by National Library of Health, China had the largest number of cases and mortality (37.0% and 39.8%, respectively) in 2020. The pandemic's pressure on healthcare systems has underscored the necessity for early and accurate diagnostics to differentiate between COVID-19 and cancer, leading to increased investments in screening technologies such as low-dose spiral CT scans, which have proven effective in detecting lung cancer at earlier stages.
The Chinese government has been proactive in addressing the rising incidence of lung cancer through various initiatives and policies. Chinese National Health Commission has recognized screening programs as part of its broader strategy to improve control and management. In addition, the inclusion of screening in national health insurance programs has made these services more accessible to a broader population, thus driving market expansion. The Healthy China Initiative 2019-2030 program, the country’s signature national domestic public health policy mandates that local governments are encouraged to promote universal opportunistic screening tailored to regional epidemiological data for cancers with high incidence rates and well-established screening methods-such as lung cancer. This approach supports early detection and treatment, significantly impacting public health outcomes.
Public awareness about lung cancer and the benefits of early detection has significantly increased in China. Awareness campaigns and educational programs, organized by both government and non-governmental organizations, have highlighted the importance of regular screening, especially among high-risk populations such as smokers and individuals with a family history of lung cancer. These initiatives have led to greater public engagement with screening programs, contributing to the market's growth.
Furthermore, the improvement and expansion of healthcare infrastructure in China, including the development of specialized centers and screening facilities, have made it easier for patients to access lung cancer screening services. This expansion supports the growth of the market by increasing the availability and accessibility of screening options. The increasing disposable income and health consciousness among the population contribute to higher utilization of screening services, including those for lung cancer.
Market Concentration & Characteristics
The market is experiencing significant innovation driven by technological advancements and increased research investment. Innovations include the development of advanced imaging techniques such as low-dose computed tomography (LDCT), which enhances early detection of lung cancer with minimal radiation exposure. AI-driven tools are also emerging, offering advanced image analysis that improves diagnostic accuracy and speed. For instance, in June 2024, DELFI Diagnostics, Inc., known for its innovative blood-based AI tests, revealed data on its FirstLook Lung test. This report highlights the test’s exceptional performance and potential in enhancing lung cancer detection. FirstLook Lung, the first validated high-sensitivity test of its kind. This advancement marks a significant step forward in bridging the gap in current screening methodologies.
The market in China has seen increased merger and acquisition (M&A) activities as companies focus on consolidating their positions and expanding their technological capabilities. Key players in the market are acquiring smaller firms specializing in advanced diagnostic technologies and AI solutions. There has been a notable trend of established diagnostic companies merging with AI startups to integrate advanced data analytics and machine learning capabilities into their screening solutions.
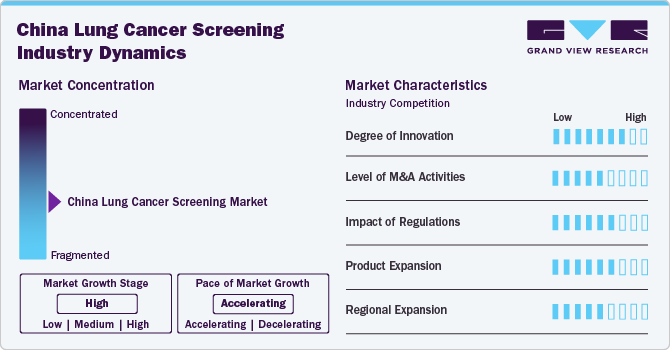
Regulatory bodies play a crucial role in shaping the approval of diagnostic solutions. The National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) oversees the approval and regulation of medical devices and diagnostic technologies. Recent regulatory initiatives have focused on streamlining approval processes for innovative screening technologies and ensuring that new products meet stringent safety and efficacy standards.
The product expansion in the China lung cancer screening market is driven by several key factors, including high disease prevalence, technological advancements, and supportive government initiatives.To address this, companies are expanding their product offerings to include advanced technologies such as low-dose computed tomography (LDCT), digital radiography, and AI-enhanced imaging systems.
China's market is substantially growing, driven by increasing regional efforts to improve healthcare infrastructure and screening programs. The government in China is significantly investing in advanced diagnostic tools and expanding access to screening services. Several provinces have launched state-funded initiatives to enhance the availability of low-dose CT scans, particularly in rural and underserved areas, to facilitate early detection and lower mortality rates. In August 2024, Chinese Hospital was designated a Center of Excellence (COE) by GO2 for Lung Cancer in recognition of its dedication to offering patient-centered, evidence-based lung cancer screening in the San Francisco area.
Cancer Insights
Non-small cell lung cancer held the largest share of 81.29% in 2023, driven by the high prevalence, advancements in diagnostic technology, supportive government policies, and improvements in healthcare infrastructure. In China, NSCLC is particularly prevalent due to high smoking rates and environmental pollution, contributing to a significant burden of disease. According to AstraZeneca, in June 2024, China records over one million new lung cancer diagnoses annually, representing over a third of global cases. Among these, Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) is the most prevalent type, with around 40% of Chinese patients exhibiting tumors with EGFR mutations. Additionally, a significant proportion of NSCLC cases are identified at advanced stages. The high incidence rates drive demand for effective screening solutions to enable early detection and improve patient outcomes.
The Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC) segment is expected to grow at the fastest growth over the forecast period. SCLC, though less common than Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC), is known for its aggressive nature and rapid progression. According to data published by National Institute of Health in October 2023, SCLC represents about 15% of all lung cancer cases in China. The growing number of SCLC diagnoses is contributing to the rising demand for effective screening solutions. The aggressive nature of SCLC necessitates early and accurate detection to improve survival rates, driving increased investment in diagnostic technologies. Advances in treatment for SCLC, including new chemotherapy regimens and targeted therapies, are also contributing to the increased focus on early detection.
Diagnosis Insights
On the basis of diagnosis, Low Dose Spiral CT (LDCT) scan held the largest share of 70.69% in 2023 and is also expected to grow at the fastest CAGR over the forecast period. LDCT is recognized for its effectiveness in detecting early-stage lung cancer, particularly in high-risk populations such as long-term smokers and individuals with a history of exposure to carcinogens. Studies, including those from the National Lung Screening Trial (NLST), have demonstrated that LDCT significantly reduces lung cancer mortality by identifying tumors at an early, more treatable stage. This high accuracy in detecting small, potentially life-threatening tumors contributes to its dominant market share.
Increased public awareness about the benefits of early lung cancer detection and the expansion of screening programs contribute to the rising demand for LDCT. Awareness campaigns and educational initiatives are encouraging more individuals to undergo regular screenings, driving the growth of LDCT in the market. A Chinese recommendation for the early detection and screening of lung cancer recommends LDCT screening for people aged 50 to 74 years who meet any of the following conditions, including passive smoking, heavy smoking, occupational exposure history, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and family history of lung cancer.
End Use Insights
Diagnostic centers held the largest share of 45.36% in 2023. Diagnostic centers are specialized facilities equipped with advanced imaging technologies and staffed by highly trained medical professionals. They offer comprehensive diagnostic services, including Low Dose Spiral CT (LDCT) scans, which are essential for the early detection of lung cancer. The concentration of specialized equipment and expertise in these centers enables accurate and efficient screenings, which is a key factor driving their significant market share. The Chinese government has actively promoted lung cancer screening programs, with diagnostic centers being central to these initiatives. Policies and recommendations from the National Health Commission support the integration of LDCT screening into routine diagnostic practices, further solidifying the role of diagnostic centers.
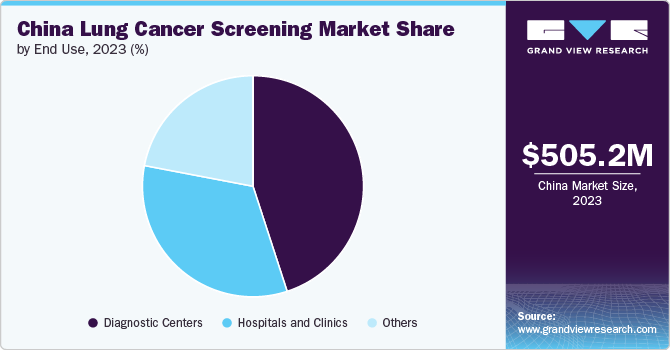
The hospitals & clinics segment is anticipated to grow at fastest growth over the forecast period. Hospitals and clinics are increasingly equipped with state-of-the-art diagnostic technologies, such as advanced Low Dose Spiral CT (LDCT) scanners and PET/CT imaging systems. These advanced tools enable precise and early detection of lung cancer, making hospitals and clinics essential in providing accurate and timely diagnoses. The integration of these technologies into hospital and clinic settings enhances their ability to manage high-risk patients and conduct large-scale screening programs. Hospitals and clinics offer a holistic approach to lung cancer care, integrating screening with treatment and follow-up services. This comprehensive model attracts patients obtaining continuity of care, from initial diagnosis to treatment and management. The ability to provide a full spectrum of services within a single facility drives the preference for hospitals and clinics over standalone diagnostic centers.
Key China Lung Cancer Screening Company Insights
The competitive scenario in the China lung cancer screening market is high, with key players such as Biodesix; DELFI Diagnostics, Inc.; GE HealthCare; Shenzhen Mindray Bio-Medical Electronics Co., Ltd.; Siemens Healthineers AG; Koninklijke Philips N.V.; CANON MEDICAL SYSTEMS CORPORATION; Medtronic; Shanghai United Imaging Healthcare Co., LTD; Freenome Holdings, Inc. holding significant positions. The major companies are undertaking various strategies such as new product development, mergers, collaborations, acquisitions, collaborations, and regional expansion to serve the unmet needs of their customers.
Key China Lung Cancer Screening Companies:
- Biodesix
- DELFI Diagnostics, Inc.
- GE HealthCare
- Shenzhen Mindray Bio-Medical Electronics Co., Ltd.
- Siemens Healthineers AG
- Koninklijke Philips N.V.
- CANON MEDICAL SYSTEMS CORPORATION
- Medtronic
- Shanghai United Imaging Healthcare Co., LTD
- Freenome Holdings, Inc.
Recent Developments
- In May 2024, Project HOPE, in partnership with the Bristol Myers Squibb Foundation, launched a groundbreaking lung cancer care program in Yunnan Province, China. This initiative aims to tackle the critical issue of early lung cancer detection and improve access to treatment in rural areas.
China Lung Cancer Screening Market Report Scope
Report Attribute
Details
Market size value in 2024
USD 554.17 million
Revenue forecast in 2030
USD 1,041.58 million
Growth rate
CAGR of 11.09% from 2024 to 2030
Actual data
2018 - 2023
Forecast period
2024 - 2030
Quantitative units
Revenue in USD million and CAGR from 2024 to 2030
Report coverage
Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends
Segments covered
Cancer, diagnosis, end use
Regional scope
China
Key companies profiled
Biodesix, DELFI Diagnostics, Inc.; GE HealthCare; Shenzhen Mindray Bio-Medical Electronics Co., Ltd.; Siemens Healthineers AG; Koninklijke Philips N.V.; CANON MEDICAL SYSTEMS CORPORATION; Medtronic; Shanghai United Imaging Healthcare Co., LTD; and Freenome Holdings, Inc.
Customization scope
Free report customization (equivalent up to 8 analyst working days) with purchase. Addition or alteration to country, regional & segment scope.
Pricing and purchase options
Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. Explore purchase options
China Lung Cancer Screening Market Report Segmentation
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis on the latest industry trends and opportunities in each of the sub-segments from 2018 to 2030. For the purpose of this study, Grand View Research has segmented the China lung cancer screening market report on the basis of cancer, diagnosis, end use, and region:
-
Screening Cancer Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
-
Non-small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
-
Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC)
-
-
Screening Diagnosis Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
-
Low Dose Spiral CT Scan
-
Chest X-ray
-
-
Screening End Use Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
-
Hospitals and Clinics
-
Diagnostic Centers
-
Others
-
Frequently Asked Questions About This Report
b. The China lung cancer screening market size was estimated at USD 505.17 million in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 554.17 million in 2024.
b. The China lung cancer screening market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 11.09% from 2024 to 2030 to reach USD 1,041.58 million by 2030.
b. Non-small cell lung cancer held the largest share of 81.29% in 2023, driven by the high prevalence, advancements in diagnostic technology, supportive government policies, and improvements in healthcare infrastructure.
b. Some key players operating in the China lung cancer screening market include Biodesix, DELFI Diagnostics, Inc., GE HealthCare, Shenzhen Mindray Bio-Medical Electronics Co., Ltd., Siemens Healthineers AG, Koninklijke Philips N.V., CANON MEDICAL SYSTEMS CORPORATION, Medtronic, Shanghai United Imaging Healthcare Co., LTD, and Freenome Holdings, Inc.
b. Key factors that are driving the market growth include including the high prevalence of lung cancer, advances in screening technology, supportive government policies, and increasing awareness about early detection.
Share this report with your colleague or friend.
![gvr icn]()
NEED A CUSTOM REPORT?
We can customize every report - free of charge - including purchasing stand-alone sections or country-level reports, as well as offer affordable discounts for start-ups & universities. Contact us now
![Certified Icon]()
We are GDPR and CCPA compliant! Your transaction & personal information is safe and secure. For more details, please read our privacy policy.
We are committed towards customer satisfaction, and quality service.
"The quality of research they have done for us has been excellent."