Agriculture Grade Zinc Chemicals Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report By Product (Zinc Oxide, Zinc Sulphate, EDTA Chelated Zinc), By Region, And Segment Forecasts, 2019 - 2025
- Report ID: GVR-3-68038-884-8
- Number of Report Pages: 109
- Format: PDF, Horizon Databook
- Historical Range: 2014 - 2017
- Forecast Period: 2019 - 2025
- Industry: Bulk Chemicals
Industry Insights
The global agriculture grade zinc chemicals market size was estimated at USD 673.8 million in 2018 and is expected to witness a CAGR of 6.3% from 2019 to 2025. Growing demand for the chemicals to maximize agricultural output per hectare from the zinc-deficit agricultural lands is expected to fuel the growth. Rising awareness about the significance of zinc chemicals in agriculture is projected to further augment the growth.
Zinc, sulphur, bentonite, and chlorine are the major raw materials used for manufacturing agriculture grade chemicals. Apart from chlorine, all the other raw materials are naturally occurring and are available in sufficient quantities. The raw materials are refined before being used as a feedstock for the production of these products.
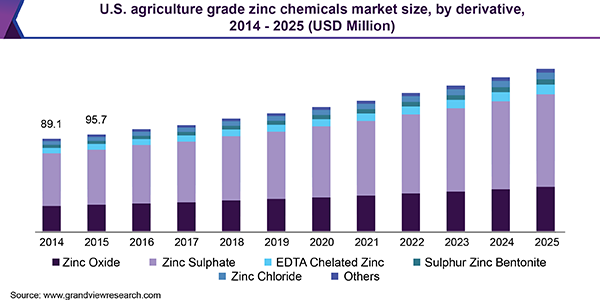
The U.S. agriculture industry was dominated by zinc sulphate with a volume share of 56.5% in 2018. The presence of vast zinc reserves in U.S. has attracted various players, such as OldBridge Chemicals, American Chemet Corporation, and Tiger Sul. U.S. was the fifth-largest producer of zinc with total production of 0.79 million tons in 2018.
Micronutrients are one of the most vital products used for manufacturing agrochemicals. They play a crucial role in maintaining the structural integrity of biological membranes. According to the International Zinc Association (IZA), zinc-binding proteins account for around 10% of all the proteins in the entire biological system. The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) has determined that almost 50% of the agricultural soils across the globe have nutrient deficiency.
The IZA has been taking initiatives to spread awareness regarding the symptoms of zinc deficiency in plants, such as leaf chlorosis (change in leaf color), bronzing of leaves, necrotic spots, and reduced stem elongation. The addition of such mineral-based products in the early stage of a disease may help prevent crop destruction.
Excess micronutrients in the soil can also adversely affect the environment, especially microorganisms and earthworms present in agricultural soils. Nutrients present in the soil often get carried away to water bodies, which harms aquatic life and also contaminates the water. Grazing livestock is also largely affected due to the mineral deposits in soil and water bodies. Agriculture grade chemical manufacturers are focusing on developing water-soluble derivatives to reduce their toxicity.
Derivative Insights
Zinc sulphate emerged as the largest consumed derivative with a volume share of 57.3% in 2018. The product is typically a granulated free-flowing powder which is applicable across dairy, cropping, and livestock industries. Fertilizer grade zinc sulphate monohydrate is observed to mix well with several products which make it suitable for agricultural application. However, mixing with substances of different particle sizes may cause segregation.
EDTA chelated zinc has emerged as an effective substitute for sulphate derivative. EDTA chelated products enhance the photosynthesis process in the crops. This derivative is gaining popularity owing to its high efficiency with minimum quantity usage. Thus, it has a high growth potential and is anticipated to register a CAGR of 6.6% from 2019 to 2025.
Regional Insights
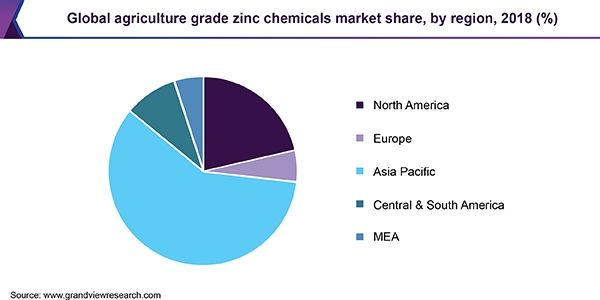
Asia Pacific dominated the agriculture grade zinc chemicals market in 2018 and is expected to growth at the fastest CAGR in the forthcoming years. The region is home to major agro economies, such as India and China. It is characterized by high zinc production, mainly in China, and the presence of stringent regulatory policies affecting the industry. Asia Pacific is expected to ascend at a CAGR of 6.7%, in terms of revenue, over the forecast period. The growth is anticipated to be driven by the advent of sustainable farming practices.
Europe has traditionally been a frontrunner in terms of advancing agrarian practices across the globe. However, compared to other parts of the world, zinc deficiency is less prominent in European soil. However, countries such as Belgium, Denmark, France, Germany, Netherlands, Poland, U.K., and Spain have registered significant micronutrient deficiency in their soils. According to the U.S. Geological Survey, Sweden was the major producer of zinc in Europe, accounting 0.22 million tons in 2018.
According to the IZA, zinc content in the French soil differs based on textural classes. For example, sandy soils contain 17 mg per kg of the product while loamy soil contains 63.5 mg per kg. Clayey soils are highly rich in zinc and contain around 98 mg per kg of the mineral. Sulphate based derivatives are commonly used to correct the deficiency in soil. Zinc nitrate is used as a substitute for its sulfate form, especially for the cultivation of maize on clayey and calcareous alluvial soils.
Agriculture Grade Zinc Chemicals Market Share Insights
Rising demand for the product in agricultural industry can mainly be attributed to poor soil nutrient content. Major agrochemical manufacturing companies such as UPL Limited and Syngenta AG are the end users of these products. The market is fragmented in nature with presence of large number of small-scale regional players and a few large companies with global supply networks. Major companies operating in the market have developed long-term contracts with leading global distributors.
Manufacturers such as IFFCO, Yara International, Zochem LLC, and EverZinc have strategically acquired different companies to enhance their product portfolio, production capacity, and geographical presence. Such mergers and acquisitions are anticipated to help companies adopt and implement new production technologies. Other relevant industry participants include Rubamin, Sulphur Mills Ltd, Aries Agro Ltd., and Prabhat Fertilizer.
Report Scope
|
Attribute |
Details |
|
Base year for estimation |
2018 |
|
Actual estimates/Historical data |
2014 - 2017 |
|
Forecast period |
2019 - 2025 |
|
Market representation |
Volume in kilotons, Revenue in USD Million & CAGR from 2018 to 2025 |
|
Regional scope |
North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Central & South America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Country Scope |
U.S., Canada, Mexico, U.K., Germany, France, Italy, China, India, Japan, Brazil, Argentina, Saudi Arabia |
|
Report coverage |
Revenue forecast, company share, competitive landscape, growth factors and trends |
|
15% free customization scope (equivalent to 5 analyst working days) |
If you need specific information, which is not currently within the scope of the report, we will provide it to you as a part of customization |
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at global, regional, and country level and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2014 to 2025. For the purpose of this study, Grand View Research has segmented the global agriculture grade zinc chemicals market report on the basis of derivative and region:
-
Derivatives Outlook (Volume, Kilotons; Revenue, USD Million, 2014 - 2025)
-
Zinc Oxide
-
Zinc Sulphate
-
EDTA Chelated Zinc
-
Sulphur Zinc Bentonite
-
Zinc Chloride
-
Others
-
-
Regional Outlook (Volume, Kilotons; Revenue, USD Million, 2014 - 2025)
-
North America
-
U.S
-
Canada
-
Mexico
-
-
Europe
-
U.K.
-
Germany
-
France
-
Italy
-
-
Asia Pacific
-
China
-
India
-
Japan
-
-
Central & South America
-
Brazil
-
Argentina
-
-
Middle East & Africa
-
Saudi Arabia
-
-
Frequently Asked Questions About This Report
b. The global agriculture grade zinc chemicals market size was estimated at USD 714.6 million in 2019 and is expected to reach USD 758.5 million in 2020.
b. The global agriculture grade zinc chemicals market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 6.3% from 2019 to 2025 to reach USD 1,036.4 million by 2025.
b. Asia Pacific dominated the agriculture grade zinc chemicals market with a share of 59.5% in 2019. This is attributable to advent of sustainable farming practices and high zinc production, mainly in China.
b. Some key players operating in the agriculture grade zinc chemicals market include IFFCO, Yara International, Zochem LLC, EverZinc, Rubamin, Sulphur Mills Ltd, Aries Agro Ltd., and Prabhat Fertilizer.
b. Key factors that are driving the market growth include rising awareness regarding benefits of zinc micro nutrient in agriculture industry and focus on improving the agricultural output per hectare of land.
We are committed towards customer satisfaction, and quality service.
"The quality of research they have done for us has been excellent."