- Home
- »
- Clinical Diagnostics
- »
-
Africa Malaria Diagnostics Market Size, Industry Report 2030GVR Report cover
![Africa Malaria Diagnostics Market Size, Share & Trends Report]()
Africa Malaria Diagnostics Market (2024 - 2030) Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report By Technology (Rapid Diagnostic Tests, Microscopy, Molecular Diagnostic Tests), By End-use (Hospitals & Clinics, Diagnostic Laboratories), By Region, And Segment Forecasts
- Report ID: GVR-4-68040-266-8
- Number of Report Pages: 125
- Format: PDF
- Historical Range: 2018 - 2022
- Forecast Period: 2024 - 2030
- Industry: Healthcare
- Report Summary
- Table of Contents
- Segmentation
- Methodology
- Download FREE Sample
-
Download Sample Report
Africa Malaria Diagnostics Market Trends
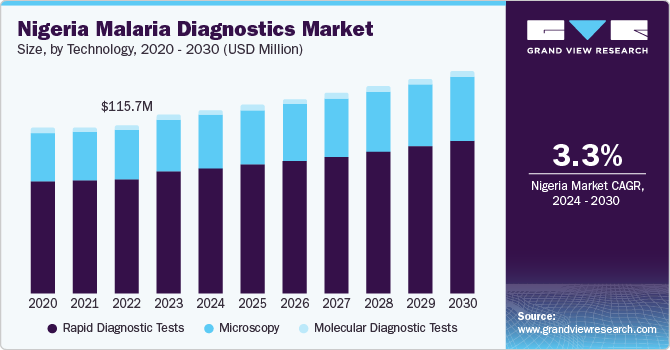
The Africa malaria diagnostics market size was estimated at USD 418.32 million in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 2.60% from 2024 to 2030. The market growth is attributed to the increasing demand for diagnostic tools in malaria-endemic countries, the initiatives undertaken by the government to curb the burden of malaria and by market players and private investors to curb the prevalence of malaria, and increasing demand for point-of-care diagnostics.
In malaria-endemic countries, especially in sub-Saharan Africa, there is a growing demand for diagnostic tools to combat the burden of malaria. This demand is driven by several factors, including the need for accurate and timely diagnosis, the emergence of drug-resistant strains of the malaria parasite, and the desire to reduce malaria-related morbidity & mortality rates.
One of the key drivers of demand for diagnostic tools in malaria-endemic countries is the growing need for accurate and timely diagnosis. Rapid Diagnostic Tests (RDTs) are increasingly being used in these settings due to their ease of use, quick results, and ability to detect malaria antigens in blood samples. For example, the use of RDTs has been instrumental in improving the diagnosis of malaria in remote and resource-limited areas. For instance, there has been a significant increase in the use of RDTs for malaria globally in recent years; according to manufacturers surveyed for the World Malaria Report 2021, 3.1 billion RDTs were sold globally between 2010 and 2020, with nearly 81% of these sales occurring in sub-Saharan African countries. During the same period, national malaria programs distributed 2.2 billion RDTs, with 88% of these being distributed in sub-Saharan Africa.
Furthermore, there is a growing awareness of the importance of early diagnosis and treatment in reducing malaria-related morbidity and mortality. This has led to an increased demand for diagnostic tools that can accurately detect malaria in its early stages. For example, light microscopy enables the detection of malaria parasites in blood samples, enabling healthcare providers to initiate treatment promptly. In addition, due to the increasing demand for diagnostic tools in malaria-endemic countries, efforts have been made to improve the availability and accessibility of these tools. For example, WHO has developed guidelines for the use of RDTs in malaria-endemic countries and tried to ensure that these tests are affordable & widely available.
In addition, in December 2022, the Nigeria government collaborated with African governments and institutions such as the African Union (AU) and Africa Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (Africa CDC) to advance common public health objectives. Since the start of the Biden-Harris Administration, Nigeria has invested nearly USD 20 billion in health programs in Africa, with over USD 2 billion dedicated to combating malaria. The Nigeria President’s Malaria Initiative (PMI) is operational in 24 African countries, working to enhance support for the health workforce. In 2021, a policy change was implemented to promote long-term investment in community health workers, ensuring access to remote areas affected by malaria. This new policy mandates partner countries across Africa to compensate community health workers using PMI funds. Since the 1950s, the Nigeria government has been actively engaged in global malaria initiatives and is currently the largest donor government to such efforts. In FY 2023, Nigeria funding for malaria control and research amounted to around USD 1 billion, marking an increase from USD 822 million in FY 2013. Furthermore, Nigeria is the leading contributor to the Global Fund to Malaria (Global Fund), which serves as the primary financier of malaria initiatives globally.
Market Concentration & Characteristics
The Africa malaria diagnostics industry shows a moderate degree of innovation, with advancements focused on enhancing test accuracy, speed, and accessibility. Innovations include the development of rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs) with improved sensitivity and specificity, as well as the integration of digital technologies for remote monitoring and data collection. These innovations aim to improve malaria diagnosis and surveillance in resource-limited settings.
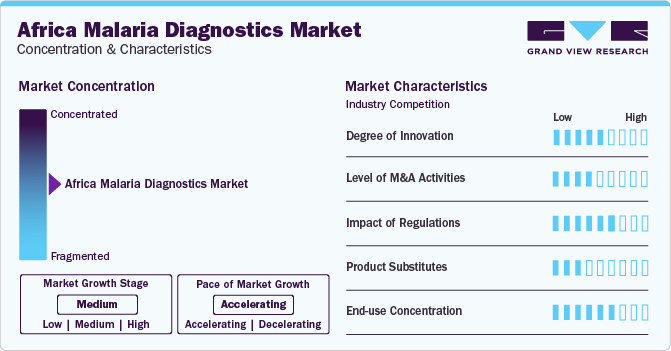
The Africa malaria diagnostics industry witnesses moderate level of merger and acquisition activities, with companies seeking to expand their product portfolios and geographic presence. Key players in the market have acquired smaller companies to gain access to new technologies and capabilities. In addition, strategic partnerships and collaborations are common in the market, enabling companies to leverage each other's strengths and enhance their market position.
In Africa malaria diagnostics industry, regulatory trends are influenced by key programs such as the WHO Product Testing Programme, WHO-FIND Lot Testing Programme, WHO Prequalification of In Vitro Diagnostics Programme (PQ), and the Global Fund/UNITAID Expert Review Panel for diagnostics. These programs play a crucial role in ensuring the quality, efficacy, and reliability of malaria diagnostic products available in the market. They provide guidance, conduct testing & evaluation, and offer prequalification services, helping streamline regulatory processes and enhance access to high-quality diagnostics in the region. Their efforts contribute significantly to the improvement of malaria diagnosis and control in Africa.
In the Africa malaria diagnostics industry, traditional microscopy and rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs) are the primary methods for diagnosing malaria. While there are no direct substitutes for these methods, advancements in molecular diagnostics offer a complementary approach. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests, although more expensive and require specialized equipment, provide higher sensitivity and can detect low levels of the malaria parasite. However, the widespread adoption of PCR in resource-limited settings like Africa is limited due to cost and infrastructure requirements.
In the Africa malaria diagnostics industry, end-user concentration is very high, with a limited number of large purchasers or users of diagnostic tests. This concentration is often seen in centralized healthcare systems or large healthcare organizations that procure and distribute diagnostic tests on a large scale. High end-user concentration can impact market dynamics, pricing strategies, and the adoption of new diagnostic technologies.
Technology Insights
The rapid diagnostic tests segment led the market in 2023 with a revenue share of 67.80% and is anticipated to grow at the fastest CAGR over the forecast period. RDTs have been a crucial tool in the fight against malaria in Africa, where reliable microscopic diagnosis is often unavailable. These tests are easier to deploy at low costs and require minimal expertise compared to traditional microscopy. However, a recent study found that RDTs may miss up to 20% of malaria cases in some regions in Africa, highlighting the need for continuous improvement in diagnostic tools.
According to WHO, over 94% of global deaths with malaria cases occur in Africa, highlighting the importance of effective diagnostic strategies. Manufacturers have reported significant sales of RDTs in Africa, with sub-Saharan African countries accounting for nearly 81% of global sales between 2010 and 2020.
The microscopy segment is anticipated to grow at a significant CAGR over the forecast period. Government initiatives are expected to offer lucrative opportunities during the forecast period. In November 2023, Muhimbili College of Health and Allied Sciences received equipment from the Nigerian government, facilitated by the Nigeria Agency for International Development (USAID) and the Nigeria President's Malaria Initiative. This equipment, valued at USD 488,000, is intended to enhance the capacity of malaria laboratory technologists in Tanzania. It will be transferred to the Ministry of Health's Colleges of Health and Allied Sciences in six regions: Mbeya, Morogoro, Dar es Salaam, Tanga, Mara, and Singida.
End-use Insights
Hospitals & clinics led the market in 2023 with a revenue share of 64.42%. Several factors drive market growth, especially in hospitals and clinics. One key factor is the high prevalence of malaria in the region, which creates a significant demand for reliable diagnostic tools. Governments and international organizations are implementing programs to improve access to malaria diagnostics in healthcare facilities.
For example, WHO’s Test, Treat, and Track strategy has been widely adopted in African countries. It emphasizes the importance of accurate diagnosis using RDTs to ensure appropriate treatment, leading to increased procurement and use of RDTs in hospitals and clinics across Africa.
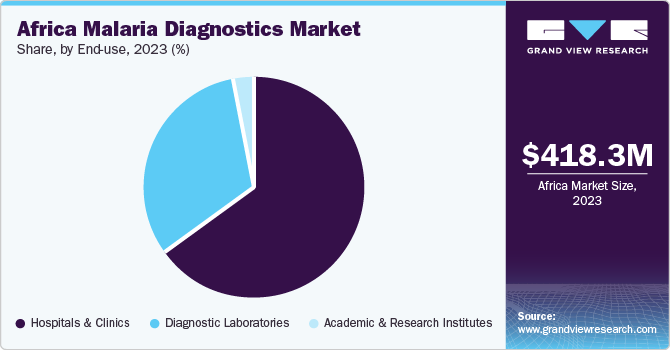
The diagnostic laboratories segment is projected to witness the fastest CAGR over the forecast period. Diagnostic laboratories in Africa may offer a range of tests, including traditional microscopy, rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs), and, in some cases, molecular diagnostics such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests. These laboratories are essential for diagnosing malaria, guiding treatment decisions, and contributing to malaria surveillance efforts. External partners and sponsors such as the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation (BMGF), Wellcome, & the Nigerian government heavily influence laboratory and diagnostic programs in Africa.
Country Insights
Nigeria Malaria Diagnostics Market Trends
The Nigeria malaria diagnostic market accounted for a 29.42% share in 2023. In Nigeria, malaria is a significant health challenge, with the country having the highest number of malaria cases in the African region and accounting for a large proportion of global malaria deaths. The WHO World Malaria Report 2021 highlighted a five-fold increase in confirmed malaria cases in Nigeria between 2011 & 2020, with over 21 million Nigerians diagnosed with malaria in 2020 alone. In addition, government initiatives will further augment the use of diagnostic kits in the country. For instance, a collaborative effort between Nigeria and the U.S. was launched in June 2022 to establish Nigeria's first Malaria Slide Bank. This initiative, funded by the Nigeria President's Malaria Initiative (PMI), aims to provide standardized, validated slide sets for malaria training and healthcare facilities. Partners involved in this project include the Walter Reed Army Institute of Research (WRAIR), the Nigeria Army Medical Research Directorate-Africa in Nigeria (USAMRD-A/N), the National Malaria Elimination Programme (NMEP), the Nigerian Ministry of Defence, and the State Ministries of Health in Benue and Akwa Ibom, supported by HJFMRI.
Democratic Republic of Congo Malaria Diagnostics Market Trends
The malaria diagnostics market in the Democratic Republic of Congo is expected to grow over the forecast period. The DRC accounts for 11% of global malaria deaths, with 60% of all hospital visits in the country attributed to malaria. Understanding malaria transmission in the DRC is crucial for efforts to eliminate malaria in sub-Saharan Africa. Besides its high disease burden, the DRC is also a bridge of transmission, connecting parasites from East and West Africa.
Tanzania Malaria Diagnostics Market Trends
Tanzania's malaria diagnostics market is growing at a moderate CAGR, with a population of nearly 60 million and approximately 93% of people living in areas where malaria is transmitted, with 96% of infections caused by Plasmodium falciparum. In 2019, the WHO estimated that Tanzania had over 6 million cases of malaria and more than 20,000 malaria-related deaths.
Uganda Malaria Diagnostics Market Trends
The malaria diagnostics market in Uganda is characterized by a high demand for accurate & reliable testing methods due to the country's high malaria burden. The market is driven by factors such as the government's efforts to control malaria, increasing awareness about the importance of early diagnosis, and the availability of funding from international organizations & donors.
South Africa Malaria Diagnostics Market Trends
The South Africa malaria diagnostics market is significant in Africa. Even though microscopy has been the traditional gold standard, its limitations, including detection thresholds and infrastructure challenges, have led to the use of RDTs in South Africa to complement microscopy in malaria diagnosis. RDTs have been particularly useful in addressing logistical difficulties, ensuring timely diagnosis and treatment under the National Malaria Diagnostic and Treatment Guidelines.
Mozambique Malaria Diagnostics Market Trends
The malaria diagnostics market in Mozambique is growing significantly over the forecast period. Despite successful malaria elimination in some countries, the disease remains a significant public health challenge in sub-Saharan Africa. Mozambique, with the fourth-highest malaria prevalence in the region, faces vulnerability due to factors such as inadequate healthcare infrastructure, limited access to prevention measures, and favorable climatic conditions for mosquito breeding.
Angola Malaria Diagnostics Market Trends
The Angola malaria diagnostics market is growing lucratively. Even though the Angolan population remains at risk for malaria, the country has experienced a gradual decrease in overall incidence. In 2020, Angola reported an estimated 7.5 million malaria cases and 13,600 deaths, compared to 5.3 million cases and 19,000 deaths in 2000, despite having a population half its current size.
Ghana Malaria Diagnostics Market Trends
The malaria diagnostics market in Ghana is growing significantly over the forecast period. Even though Ghana has made significant progress in reducing malaria, with malaria-attributable deaths decreasing from 19% in 2010 to 1.5% in 2018, the disease remains a significant cause of mortality in the country. To enhance malaria service delivery, PMI Impact Malaria (IM) has worked with Ghana's NMCP and Regional Health Administration (RHA) to conduct health facility-based malaria case management training for healthcare workers. IM collaborated with the RHA to identify districts & facilities with high malaria burdens, selecting ten facilities per region for immediate training based on adverse malaria indicators.
Key Africa Malaria Diagnostics Company Insights
Some of the leading players operating in the Africa malaria diagnostics industry include Abbott, Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., Premier Medical, Sysmex Corporation and Zephyr Biomedicals - A Division of Tulip Diagnostics Ltd, India. Key players are using existing customer bases in the country to prioritize high-quality standards and gain high-market-size access. This strategy is useful for brands that have already built trust in the market. These players are heavily investing in advanced technology and infrastructure, allowing them to process & analyze a large volume of samples efficiently. Moreover, companies undertake various strategic initiatives with other companies and distributors to strengthen their market presence.
SHERLOCK BIOSCIENCES and Eiken Chemical Co., Ltd are some of the emerging market participants in the Africa malaria diagnostics industry. These companies focus on achieving funding support from government bodies and healthcare organizations aided with novel product launches to capitalize on untapped avenues.
Key Africa Malaria Diagnostics Companies:
- Abbott
- Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.
- Premier Medical
- Sysmex Corporation
- Zephyr Biomedicals - A Division of Tulip Diagnostics Ltd, India
- SHERLOCK BIOSCIENCES
- Eiken Chemical Co., Ltd.
- ARKRAY, Inc.
- Meril Life Sciences Pvt. Ltd.
- SD Biosensor, Inc.,
- Advy Chemical Private Limited
Recent Developments
-
In October 2023, South Korean in-vitro diagnostics maker Noul Co signed a sales deal in Angola, valued at around 2 billion won (USD 1.4 million), which involves the company's malaria diagnostic platform. Noul Co. also has a contract with a medical device wholesaler in Angola, a country close to Nigeria, comprising the world's highest number of malaria cases. The contract includes the supply of the automated diagnostic platform miLab and malaria diagnostic cartridges through 2028
-
In November 2022, Sherlock Biosciences announced a licensing agreement with Shanghai-based Tolo Biotech. This agreement grants both companies co-exclusive rights to Cas12 and Cas13 CRISPR diagnostic methods in markets outside of Nigeria and Greater China. As the only two companies with rights to these method patents in the diagnostics market, this agreement strengthens the collaboration between Sherlock and Tolo, providing them with the most comprehensive portfolio of diagnostic CRISPR patents
Africa Malaria Diagnostics Market Report Scope
Report Attribute
Details
Market size value in 2024
USD 426.91 million
Revenue forecast in 2030
USD 498.12 million
Growth rate
CAGR of 2.60% from 2024 to 2030
Historic data
2018 - 2022
Base year for estimation
2023
Forecast period
2024 - 2030
Quantitative units
Revenue in USD million and CAGR from 2024 to 2030
Report coverage
Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends
Segments covered
Technology, end-use, country
Regional scope
Africa
Country scope
Nigeria; Democratic Republic of The Congo; United Republic of Tanzania; Uganda; South Africa; Mozambique; Angola; Ghana; Botswana; Namibia
Key companies profiled
Abbott; Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.; Premier Medical; Sysmex Corporation; Zephyr Biomedicals - A Division of Tulip Diagnostics Ltd, India; SHERLOCK BIOSCIENCES; Eiken Chemical Co., Ltd.; ARKRAY, Inc.; Meril Life Sciences Pvt. Ltd.; SD Biosensor, Inc.; Advy Chemical Private Limited
Customization scope
Free report customization (equivalent up to 8 analysts working days) with purchase. Addition or alteration to country, regional & segment scope.
Pricing and purchase options
Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. Explore purchase options
Africa Malaria Diagnostics Market Report Segmentation
This report forecasts revenue growth at regional and country level and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2018 to 2030. For this study, Grand View Research has segmented the Africa malaria diagnostics market report based on technology, end-use, and country.
-
Technology Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
-
Rapid Diagnostic Tests
-
Microscopy
-
Molecular Diagnostic Tests
-
-
End-use Outlook (Revenue, USD Million; 2018 - 2030)
-
Hospitals & Clinics
-
Diagnostic Laboratories
-
Academic and Research Institutes
-
-
Country Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2018 - 2030)
-
Africa
-
Nigeria
-
Democratic Republic of The Congo
-
United Republic of Tanzania
-
Uganda
-
South Africa
-
Mozambique
-
Angola
-
Ghana
-
Botswana
-
Namibia
-
Rest of Africa
-
-
Frequently Asked Questions About This Report
b. The Africa malaria diagnostics market size was estimated at USD 418.32 million in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 426.91 million in 2024.
b. The Africa malaria diagnostics market is expected to witness a compound annual growth rate of 2.60% from 2024 to 2030 to reach USD 498.12 million in 2030.
b. Based on technology, rapid diagnostic tests (RDT) segment held the largest share of 67.80% in 2023. These tests are easier to deploy at low cost and require minimal expertise compared to traditional microscopy.
b. Some key players operating in the Africa malaria diagnostics market include Abbott, Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., Premier Medical, Sysmex Corporation., Zephyr Biomedicals - A Division of Tulip Diagnostics Ltd, India, SHERLOCK BIOSCIENCES, Eiken Chemical Co., Ltd., ARKRAY, Inc., Meril Life Sciences Pvt. Ltd., SD Biosensor, Inc., Advy Chemical Private Limited
b. Key factors driving the Africa malaria diagnostics market growth include increasing demand for diagnostic tools in malaria-endemic countries, government initiatives to curb the burden of malaria, initiatives by market players and private investors to curb the prevalence of malaria, and increasing demand for point-of-care diagnostics
Share this report with your colleague or friend.
Need a Tailored Report?
Customize this report to your needs — add regions, segments, or data points, with 20% free customization.

ISO 9001:2015 & 27001:2022 Certified
We are GDPR and CCPA compliant! Your transaction & personal information is safe and secure. For more details, please read our privacy policy.
Trusted market insights - try a free sample
See how our reports are structured and why industry leaders rely on Grand View Research. Get a free sample or ask us to tailor this report to your needs.