Plating on Plastics Market - What’s Making It POP?
Ever seen those attractive car logos on fancy vehicles? They look so shiny, so attractive, and of the highest quality. Or even various types of handles and knobs on appliances. Manufacturers nowadays try to offer the most unique and elegant looking products in this regard. Would you believe that these products are made of plastic at its core, and that they are just coated with metallic substances? Well, metal plated plastics have achieved widespread popularity these days, owing to rapid progressions in polymer chemistry coupled with developing production technologies. That is why we see many areas of application for plating on plastics market, such as automotive, electronics, utilities and other consumer goods.
Plating on plastics has been a concept that goes a long way back to the 1960s, being practiced in Europe and North America. However, achieving a strong bond between metallic coating and the plastic substrate proved to be extremely hard for manufacturers, which can explain its low level of acceptance in those days. However, the adhesive properties of plastic were enhanced through the implementation of a chromic acid-based etchant that was used for the surface treatment on acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS), a thermoplastic polymer. The process found usage first in the automotive industry in the 1970s, and a variety of areas such as plumbing, electronics and household product manufacturers adopted it in the 70s and 80s.
There are a number of resins that are used for plating on plastic applications; however, 90% of these applications still make use of ABS as the resin. The product has an acrylonitrile-styrene matrix which is evenly distributed with butadiene rubber, which leads to effective plating. The butadiene is etched out from the matrix, leaving microscopic holes that are utilized as bonding sites by the plate. Other factors that have encouraged the large scale of ABS are the ease of molding, high metallic adhesion, affordability and low coefficient of thermal expansion.
Other resins that may be used for the plating on plastic process include:
-
PEI (polyetherimide),
-
PBT (polybutylene terephthalate),
-
LCP (liquid crystal polymer),
-
PEEK (polyether ether ketone), and
-
nylon/polyamide, among others.
It is important to note that PEEK and polypropylene can only be plated in a blended form. ABS polycarbonate (ABS/PC) is expected to witness good demand in the plating on plastics market in the coming years. The blend contains 40-60% of ABS, while the remaining is made up of PC. This mixture offers high ductility and strength, and can be made use of in extreme temperatures.
A typical plating on plastic process consists of the following steps, although some steps may vary according to the need of the product:
-
Cleaning - Requires a mild alkaline, or in certain instances, a chromic acid solution
-
Pre-dipping - Helps improve the surface of poorly molded, highly stressed parts. Also makes it easier for etchant to react and attack the surface
-
Etching - Etchants generally consist of sulfuric acid or chromium trioxide solutions, which help to increase the substrate surface, thus enhancing liquid absorption.
-
Conditioning - An optional step in the plating on plastic process, this helps in promoting a more uniform absorption during the activation stage
-
Neutralizing - Neutralizers such as sodium bisulfite can help ensure the elimination of any excess etchant.
-
Pre-activating - Pre-activator helps in facilitating absorption during the activation stage of the plating on plastic process. They work well with polypropylene or polyphenylene oxide.
-
Activating - Involves the usage of low-concentration precious metal liquid activator, which serves as a catalyst during plating. Typical metals found in activators include platinum, gold and palladium.
-
Accelerating - Accelerators removes excess stannous hydroxide from the part, and also prevents skip plating occurrence during the plating on plastics process.
-
Bath immersion - After rinsing, the plastic parts are placed in an electroless bath to deposit a thin metal coating. Nickel is generally used in the process, although some instances utilize copper.
When it comes to the type of metal used in the plating on plastics process, chrome and nickel have seen huge demand from various industries. The former offers good surface finish, aesthetic appeal and rust resistance to the substrate, and is used for plating arm rests, grills and motorbike parts. Trivalent chrome finds extensive usage in these applications as it is environment friendly. With regards to nickel, it is used mainly for decorative purposes in the automotive sector, where it is used in exterior and interior vehicle parts such as door handles, bumpers, emblems, wheels and gear shift knobs, among others. Copper has also seen significant growth in demand in the plating on plastics market, mainly from the electronics industry, where high electrical conductivity is required in many products.
Global POP market revenue by application, 2016 (%)
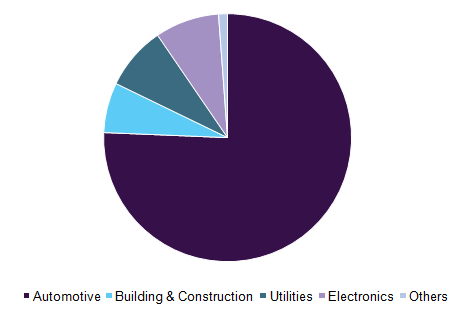
Innumerable advantages offered by the finished material are creating huge demand for the overall plating on plastics industry. Plastic has added benefits over metals as it is lighter, corrosion resistant, and inexpensive. Furthermore, plating them with a metal such as chrome, nickel, copper and others enhances the overall strength and appearance of the finished product. Additionally, metal plating provides an impression of premium quality to the product and also delivers design freedom to the manufacturers.
However, certain complications arise while plating plastics. They are electrically non-conducive and are unable to withstand the process of being immersed in a metal solution. To overcome these problems substrate etching and electroless plating were developed to plate plastic substrates. Manufacturers majorly prefer ABS plastic as it cheaper, easy to mold and has lesser coefficient of thermal expansion. All over plating and selective plating are majorly practiced, wherein all over plating metal is deposited over the surface with a thickness of 40 micro inches to 2,000 micro inches. All over plating option is typically the most cost-efficient form.
Ongoing research & development activities in the plating on plastics field are focusing on new production technologies. Chromium free etchant is a technology which provides freedom from carcinogenic hexavalent chromium, and leads to a fume free operation. This technology is expected to be widely adopted in Europe as it satisfies the norms laid by REACH. Double layer nickel systems and micro-discontinuous chromium systems are another form of technological advancements occurred into this industry.
Major competitors in the plating on plastics market include Atotech, Galva Decoparts Pvt. Ltd., Dow Chemicals, Sharretts Plating, and Cybershield Inc., along with other regional competitors. These companies are investing in developing newer technology, along with acquisition of chemical manufacturers, in order to stake claim in the global market.
 In-depth report on global plating on plastics (POP) market market by Grand View Research:
In-depth report on global plating on plastics (POP) market market by Grand View Research:
https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/plating-on-plastics-pop-market
To schedule a free market intelligence database demo, please complete the form below:
Service Guarantee
-
Insured Buying
This report has a service guarantee. We stand by our report quality.
-
Confidentiality
Your transaction & personal information is safe and secure.
-
Custom research service
Design an exclusive study to serve your research needs.
-
24/5 Research support
Get your queries resolved from an industry expert.